Related products
Secondary antibodies resources
Alexa Fluor secondary antibodies
Biotinylated secondary antibodies
Enhancing Detection of Low-Abundance Proteins
9 tips for detecting phosphorylation events using a Western Blot
Western Blotting with Tissue Lysates
Immunohistochemistry introduction
Immunohistochemistry and Immunocytochemistry
Immunohistochemistry troubleshooter
Chromogenic and Fluorescent detection
Preparing paraffin-embedded and frozen samples for Immunohistochemistry

Rabbit monoclonal antibodies
Volume KD (%)
anti acetyl histone h3 antibody 20 -; histone h3 antibody 210 20; Rabbit monoclonal antibody 260 18; ; rabbit monoclonal antibodies 70 20; Monoclonal rabbit 70 16; Rabbit monoclonal 90 12; anti cd3 antibody 280 28; anti cd28 antibody 20 -; anti pd1 antibody 50 35; anti human pd l1 antibody 30 1; Anti ctla4 antibody 50 29; anti cd20 antibody 70 33; ; anti cd56 antibody 20 0; Anti cd69 antibody 20 0; l plastin antibody 20 0; anti cd3 monoclonal antibody 90 32; anti cd3 antibody 260 28; ; anti-cd3 antibody 90 21; Mmp9 antibody 90 14; Anti her2 antibody 40 37; ezh2 antibody 90 13; rabbit monoclonal antibody 210 11; histone h3 antibody 210 20; anti acetyl histone h3 antibody 20 0; phospho akt antibody 70 11; phospho erk antibody 70 26; crp elisa 70 15; timp1 elisa 30 12; fibrinogen elisa 50 2; ki67 antibody 320 22; anti ki67 40 21
her2 expression 30 33; Il2 antibody 30 0; ; tnf alpha antibody 260 17
, anti tnf alpha antibody 170 12; e cadherin antibody 170,24; beta catenin antibody 170, 17; ZO-1 antibody zo-1 antibody 110, 24; claudin 1 antibody 30, 21; Vimentin antibody 320, 24, vimenin phosphorylation 20, 0; cytokeratin 5 antibody 90, 16; cytokeratin 14 antibody, 50, 16; cytokeratin
18 antibody 50, 10; cytokeratin 7 antibody 40, 16; gm130 100, 5, protein kinase C antibody 40, 9; gm130 110, 5; protein kinase c antibody 40, 9.
The benefits of rabbit monoclonal antibodies
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies offer significant advantages over mouse monoclonal antibodies, particularly in their unique ability to recognise epitopes on human antigens that are often non-immunogenic in mice due to difference in immune system diversity. First developed and optimised in the 1990s, rabbit monoclonal antibodies are distinguished by their exceptionally high affinity, specificity, and ability to target a wider range of epitopes. These qualities make them effective for a wide range of research applications.
St John’s Laboratory provides a comprehensive portfolio of over 7,600 rabbit monoclonal antibodies validated across a spectrum of applications, including immunohistochemistry (IHC), ELISA, Western blot (WB), and immunofluorescence (IF). Our antibodies support research in oncology, signal transduction, post-translational modifications (PTMs) and other diverse research areas.
Key benefits of the rabbit monoclonal antibody design:
- Broader epitope recognition: Rabbits generate a more diverse antibody repertoire compared to mice. Through somatic gene conversion and hypermutation, they recognise a wider variety of epitopes — even those poorly immunogenic in rodents. They also exhibit reduced immunodominance, resulting in antibody generation against multiple, non-dominant regions of an antigen.
- High sensitivity to human protein targets: Studies consistently demonstrate that rabbit monoclonal antibodies exhibit higher sensitivity to certain human antigens, owing to their higher affinity and broader epitope recognition. This makes them ideal for detecting low-abundance targets or working with limited, precious tissue samples.
- Higher antibody titres: Rabbits can produce high-affinity antibodies with robust titres. This increases the chances of finding the perfect antibody for cloning and production.
- Compatible with mouse samples: The rabbit monoclonal format reduces the risk of cross-reactivity with endogenous mouse antigens, often resulting in lower background signals in mouse tissue models.
- Excellent signal-to-noise ratio: Characterised by inherently low background noise and high binding affinity, rabbit monoclonals deliver a superior signal-to-noise ratio, making them particularly well-suited for sensitive applications like immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Applications of rabbit monoclonal antibodies
Stemming from the unique properties of the rabbit immune system, rabbit monoclonal antibodies deliver several advantages for research applications.
Detecting post-translational modifications (PTMs)
Post-translational modifications occur after translation from mRNA and significantly impact a protein's structure, stability, location, and its interactions with other molecules, ultimately impacting its functionality.
Rabbit monoclonals are highly effective in recognising small epitopes, making them key reagents for detecting specific PTMs – such as specific phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation, and sumoylation sites.
Histone acetylation detection
- Acetyl histone h3 antibody (Anti-Acetyl-Histone H3-K56 antibody [S4732RM] (STJ11104732)
Histone H3, one of the five main histones that contribute to chromatin structure in eukaryotes, plays a crucial role in gene regulation. Post-translational modification (PTM) through acetylation at lysine 56 (H3K56Ac) signals the synthesis of new histones, and this process is highly regulated during the cell cycle.
A valuable tool for studying chromatin biology and cell cycle research is anti acetyl histone h3 antibody (K56) [S4732RM] (STJ11104732). This antibody enables researchers to monitor replication-coupled histone deposition, evaluate the function of histone chaperones, and assess DNA damage response.
Detecting phosphorylation EGFR protein expression status
Elevated levels of phosphorylated forms of the transmembrane protein EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) have been observed in several cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer. Sustained phosphorylation, particularly at tyrosine 1068 (pTyr1068), along with other phosphorylation sites, is associated with increased receptor activation and enhanced downstream signalling. This activation is linked to aggressive tumour characteristics and poorer clinical outcomes.
Anti-Phospho-EGFR-Y1068 antibody [S0MR] (STJ11102550) allows the detection of active EGFR signalling through a specific phosphorylation site, offering insights into receptor activation patterns, tumour biology, and potential therapeutic responses.
SUMOylation
The PTM modification SUMOylation has become increasingly recognised for its ability to regulate protein stability, cellular localisation and protein-protein interactions affecting multiple processes from transcription to DNA repair.
SUMOylation is a PTM involving the covalent attachment of small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMO) proteins to the lysine residue of target proteins via SUMO E3 ligases.
- St John’s rabbit monoclonal antibodies target SUMO E3 ligases, which are dysregulated or upregulated in disease contexts, such as PIAS1 and PIAS2.
St John’s rabbit monoclonal antibodies detect:
PIAS1 Anti-Recombinant-PIAS1 antibody [RM1F78] (STJA0023171)
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies for IHC (Immunohistochemistry) applications
Rabbit monoclonals offer distinct advantages in IHC:
- Increased sensitivity with no loss of specificity.
- Permit higher working dilutions, making them more cost-effective for routine use.
- Compatible with various tissue fixations, including formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue, with minimal pre-treatment.
- Allow for dual staining with mouse monoclonals on the same tissue sample.
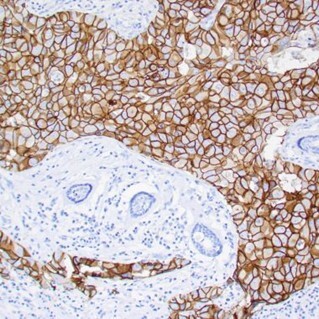
Assessing HER2 expression
Understanding HER2 (Erbb2) through immunohistochemistry (IHC) is critical for deciphering cancer biology and characterising tumour models, offering insights into disease progression. This analytical approach allows researchers to precisely characterise tumour subtypes, explore the intricate signalling pathways driven by HER2 overexpression, and identify novel biomarkers.
Anti HER2 antibody
The anti HER2 antibody (anti-ERBB2 antibody) (ECD) [ZR5] (STJ180123) . This is a valuable tool for research due to its precise targeting of the HER2/ErbB2 protein's extracellular domain. Its utility in immunohistochemistry (IHC) enables detailed spatial and quantitative analysis in tissue samples, enhancing the understanding of tumour progression and advancing the understanding of signal transduction.
IHC using Ki67 antibody
KI67 is an important nuclear protein, associated with cellular proliferation and ribosomal RNA transcription. Ki67 serves as an important marker for cell proliferation and is essential in evaluating cellular activity in different pathological tissues. By identifying cells actively progressing through the cell cycle, researchers can gain crucial insights into underlying biological mechanisms, evaluate the efficacy of experimental interventions in preclinical models, and further characterise tumour heterogeneity, thereby advancing the understanding of various diseases at a molecular and cellular level.
Anti Ki67
The Ki-67 antibody [ZR433] (STJ180649) is a valuable tool for immunohistochemistry (IHC) research applications. The Ki 67 antibody clone excels at accurately detecting and quantifying the Ki-67 proliferation marker in tissue samples. With its strong specificity and sensitivity for IHC, it serves as an excellent reagent for exploring cellular proliferation dynamics, understanding disease mechanisms in various research settings.
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies from St John’s Laboratory are widely used in cancer research and cell biology due to their superior sensitivity, specificity, and performance across IHC, WB, ELISA, and IF.
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies for IHC
| Target | Rabbit monoclonal antibody from St John’s Laboratory | Research applications |
|---|---|---|
| CD3 | anti CD3 monoclonal antibody : Anti-CD3 antibody [ZR414] (STJ180634) | Lymphocyte profiling |
| CD20 | anti CD20 antibody : Anti-CD20 antibody [ZR243] (STJ180556) | Lymphocyte profiling |
| CD69 | anti CD69 antibody : Anti-CD69 antibody (62-199 aa) [SRM] (STJ11107231) | Activation markers |
| LCP1 | LCP1 antibody (l plastin antibody) : Anti-Recombinant-LCP1 antibody [RM1P11] (STJA0023896) | Hematopoietic & metastasis markers |
| MMP9 | MMP9 antibody : Anti-Recombinant-MMP9 antibody [RM1P48] (STJA0023933) | Extracellular matrix |
| EZH2 (H3K27me3) | EZH2 antibody : Anti-EZH2 antibody (C-Term) [ZR150] (STJ180568) | Chromatin organisation; epigenetics |
| TNF-α | TNF alpha antibody (anti TNF antibody) : Anti-TNF-alpha antibody (80-235) [S5294RM] (STJ11105294) | Immunology |
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies for flow cytometry
Unlock the potential of single-cell analysis for your immunology research with our extensive range of flow cytometry antibodies. Designed for precision and reliability, our antibodies are available with various conjugation types, including popular fluorophores like FITC, PE, APC, and their tandem dye variations, ensuring flexibility for your multi-colour panel designs.
Selection of commonly targeted immune cell markers and their associated antibodies for flow cytometry:
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies for flow cytometry
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies for Western blot applications
| Target | Rabbit monoclonal antibody from St John’s Laboratory | Research applications |
|---|---|---|
| AKT | Phospho-specific detection using phospho AKT antibody Threonine 308: Anti-Phospho-Akt-T308 antibody [S4MR] (STJ11103774) Different sites of phosphorylation/ phospho AKT antibody for Serine 473 (Ser473): Anti-Recombinant-Phospho-AKT-S473 antibody [SR0524] (STJA0010524) The Phospho-AKT (Thr450) antibody specifically recognises Akt1 only when it is phosphorylated at the threonine 450 position.Anti-Phospho-AKT1-T450 antibody [S2MR] (STJ11102572) Antibodies are available for various phosphorylation sites of different AKT isoforms (AKT1, AKT2, AKT3) as well as for their non-phosphorylated forms. | Signal Transduction (site-specific detection) |
| ERK | Phospho-specific detection using phospho ERK antibody
Anti-Phospho-MAPK1/MAPK3-T202/Y204 & T185/Y187 antibody [S8MR] (STJ11102568). Detects p44 and p42 MAP Kinase when they are phosphorylated at Thr202 and Tyr204.
Antibodies are also available for non-phosphorylated forms of ERK1/2. | Signal Transduction (site-specific detection) |
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies for ELISA
| Target | Rabbit monoclonal antibody from St John’s Laboratory | Research applications |
|---|---|---|
| CRP | For CRP elisa: Anti-CRP antibody (1-50) (STJ118105) | Inflammation, metabolism |
| TIMP1 | For TIMP1 elisa: Anti-TIMP1 antibody (1-100) [S6MR] (STJ11102206) | Extracellular matrix regulation |
| Fibrinogen (α-chain) | For fibrinogen ELISA: ( detecting the alpha chain component of fibrinogen)Anti-Fibrinogen alpha chain antibody (700-800) [S3MR] (STJ11103073) | Haemostasis |
Rabbit monoclonal antibodies for immunofluorescence staining
| Target | Rabbit monoclonal antibody from St John’s Laboratory | Research applications |
|---|---|---|
| E cadherin | Anti E cadherin antibody | Marker of epithelial integrity and Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Important in: Cell-cell communication, developmental biology, extracellular matrix organisation, disease |
| Beta catenin | Anti Recombinant beta catenin antibody [SR0543] (STJA0010543) | Marker of epithelial integrity and Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Important in: Cell-cell communication, developmental biology, extracellular matrix organisation, disease |
| ZO-1 | Anti Recombinant ZO-1 antibody tight junction protein antibody [SR0620] (STJA0010620) | Tight junction protein in epithelial barriers.
Important in: Cell-cell communication, vesicle-mediated transport, extracellular matrix organisation, disease |
| Claudin-1 | Anti-Recombinant Claudin 1 antibody [SR0646] (STJA0010646) | Transmembrane protein, regulating permeability in tight junctions. Important in: Cell-cell communication, vesicle-mediated transport, extracellular matrix organisation, disease |
| Cytokeratin | Cytokeratin 5 antibody (KRT5 antibody), cytokeratin 7 antibody, Anti-Recombinant cytokeratin 14 antibody [RM1K42] (STJA0023531), Anti-Recombinant cytokeratin 18 antibody [RM1K42] (STJA0023531) | Structural markers of epithelial differentiation. Important in: Extracellular matrix organisation, cell-cell communication, developmental biology, disease |
| GM130 | Anti Recombinant GM130 antibody | Golgi matrix protein involved in vesicle trafficking. Important in: Organelle biosynthesis and maintenance (Golgi), vesicle mediated transport and protein localisation |
| CPSF3 | Anti-Recombinant-CPSF3 antibody [RM2RM44] (STJA0026503) | Involved in mRNA 3′-end cleavage and polyadenylation. Important in: Metabolism of RNA |
| PRKCA | Anti- Protein kinase C antibody PRKCA antibody [M499] (STJA0005532) | Multifunctional kinase involved in signalling, apoptosis, and autophagy. Important in: Signal transduction, cellular responses to stimuli, programmed cell death, autophagy, cell cycle, disease |
Featured products
SARS-CoV-2 related antibodies
Anti-Phospho-EGFR antibodies
Anti Aggrecan antibodies
Anti-Phospho-AKT1 antibodies
Anti-MKI67 antibodies
| Anti-MKI67 antibody (STJA0006295) | IHC/IF |
| Anti-MKI67 antibody (1200-1300) (STJ11104589) | IHC-P/IF/ICC/ELISA |
Anti-METTL3 antibodies
Discover the difference: St John’s Monoclonal Rabbit Antibodies?
Advance your research with St John’s Laboratory highly sensitive, epitope-diverse, and fully validated rabbit monoclonal antibodies tailored for your research needs. Designed to meet your specific research needs, whether you're investigating post-translational modifications, tumuor biology, or protein-protein interactions, our antibodies deliver.
- Unmatched sensitivity and specificity
- Broad application coverage, across Western Blot (WB), ELISA, IHC, ICC/IF, IP, Flow Cytometry
- Reduced background and cross-reactivity
- Proven performance in complex biological systems
Explore our full range of 7,600+ rabbit monoclonal antibodies today to find the perfect antibody candidate for your IHC, PTM, cancer biology, and molecular signalling research!
For Research Use Only - All products are intended for research purposes and are not for use in diagnostic procedures