| Host: | Goat |
| Applications: | Pep-ELISA/WB/IF/FC |
| Reactivity: | Human/Mouse/Rat |
| Note: | STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description : | Goat polyclonal antibody anti-RXR alpha (Internal) is suitable for use in ELISA, Western Blot, Immunofluorescence and Flow Cytometry research applications. |
| Clonality : | Polyclonal |
| Conjugation: | Unconjugated |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Formulation: | 0.5 mg/ml in Tris saline, 0.02% sodium azide, pH7.3 with 0.5% bovine serum albumin. NA |
| Purification: | Purified from goat serum by ammonium sulphate precipitation followed by antigen affinity chromatography using the immunizing peptide. |
| Concentration: | 0.5 mg/mL |
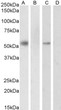
| Dilution Range: | Peptide ELISA: antibody detection limit dilution 1:32000.WB: Approx 55-60kDa band observed in nuclear lysates of cell lines HeLa and K562 (calculated MW of 50.8kDa according to NP_002948.1). This molecular weight is routinely observed by other s |
| Storage Instruction: | Store at-20°C on receipt and minimise freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Gene Symbol: | RXRA |
| Gene ID: | 6256 |
| Uniprot ID: | RXRA_HUMAN |
| Immunogen Region: | Internal |
| Accession Number: | NP_002948.1 |
| Specificity: | This antibody is expected to recognise an epitope corresponding to aa 14-28 of human RXR alpha protein and does not cross-react with either RXR beta or gamma. |
| Immunogen Sequence: | CQVNSSLTSPTGRGSM |
| Post Translational Modifications | Acetylated by EP300.acetylation enhances DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues mainly in the N-terminal modulating domain. Constitutively phosphorylated on Ser-21 in the presence or absence of ligand. Under stress conditions, hyperphosphorylated by activated JNK on Ser-56, Ser-70, Thr-82 and Ser-260. Phosphorylated on Ser-27, in vitro, by PKA. This phosphorylation is required for repression of cAMP-mediated transcriptional activity of RARA. Ubiquitinated by UBR5, leading to its degradation: UBR5 specifically recognizes and binds ligand-bound RXRA when it is not associated with coactivators (NCOAs). In presence of NCOAs, the UBR5-degron is not accessible, preventing its ubiquitination and degradation. Sumoylation negatively regulates transcriptional activity. Desumoylated specifically by SENP6. |
| Function | Receptor for retinoic acid that acts as a transcription factor. Forms homo- or heterodimers with retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and binds to target response elements in response to their ligands, all-trans or 9-cis retinoic acid, to regulate gene expression in various biological processes. The RAR/RXR heterodimers bind to the retinoic acid response elements (RARE) composed of tandem 5'-AGGTCA-3' sites known as DR1-DR5 to regulate transcription. The high affinity ligand for retinoid X receptors (RXRs) is 9-cis retinoic acid. In the absence of ligand, the RXR-RAR heterodimers associate with a multiprotein complex containing transcription corepressors that induce histone deacetylation, chromatin condensation and transcriptional suppression. On ligand binding, the corepressors dissociate from the receptors and coactivators are recruited leading to transcriptional activation. Serves as a common heterodimeric partner for a number of nuclear receptors, such as RARA, RARB and PPARA. The RXRA/RARB heterodimer can act as a transcriptional repressor or transcriptional activator, depending on the RARE DNA element context. The RXRA/PPARA heterodimer is required for PPARA transcriptional activity on fatty acid oxidation genes such as ACOX1 and the P450 system genes. Together with RARA, positively regulates microRNA-10a expression, thereby inhibiting the GATA6/VCAM1 signaling response to pulsatile shear stress in vascular endothelial cells. Acts as an enhancer of RARA binding to RARE DNA element. May facilitate the nuclear import of heterodimerization partners such as VDR and NR4A1. Promotes myelin debris phagocytosis and remyelination by macrophages. Plays a role in the attenuation of the innate immune system in response to viral infections, possibly by negatively regulating the transcription of antiviral genes such as type I IFN genes. Involved in the regulation of calcium signaling by repressing ITPR2 gene expression, thereby controlling cellular senescence. |
| Protein Name | Retinoic Acid Receptor Rxr-AlphaNuclear Receptor Subfamily 2 Group B Member 1Retinoid X Receptor Alpha |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-1368082Reactome: R-HSA-1368108Reactome: R-HSA-159418Reactome: R-HSA-192105Reactome: R-HSA-193368Reactome: R-HSA-193807Reactome: R-HSA-1989781Reactome: R-HSA-200425Reactome: R-HSA-211976Reactome: R-HSA-2151201Reactome: R-HSA-2426168Reactome: R-HSA-381340Reactome: R-HSA-383280Reactome: R-HSA-400206Reactome: R-HSA-400253Reactome: R-HSA-4090294Reactome: R-HSA-5362517Reactome: R-HSA-5617472Reactome: R-HSA-9029558Reactome: R-HSA-9029569Reactome: R-HSA-9031525Reactome: R-HSA-9031528Reactome: R-HSA-9616222Reactome: R-HSA-9623433Reactome: R-HSA-9632974Reactome: R-HSA-9707564Reactome: R-HSA-9707616Reactome: R-HSA-9839394Reactome: R-HSA-9844594 |
| Cellular Localisation | NucleusCytoplasmMitochondrionLocalization To The Nucleus Is Enhanced By Vitamin D3Nuclear Localization May Be Enhanced By The Interaction With Heterodimerization Partner VdrTranslocation To The Mitochondrion Upon Interaction With Nr4a1Increased Nuclear Localization Upon Pulsatile Shear Stress |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Retinoic Acid Receptor Rxr-Alpha antibodyAnti-Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 2 Group B Member 1 antibodyAnti-Retinoid X Receptor Alpha antibodyAnti-RXRA antibodyAnti-NR2B1 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org