| Tissue Specificity | Expressed in neuronal cells. Expressed in macrophages (at protein level). |
| Post Translational Modifications | Glycosylations at Asn-46, Asn-90 and Asn-133 are essential for TMEM35A/NACHO-mediated proper subunit assembly and trafficking to the cell membrane. |
| Function | Component of neuronal acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) that function as pentameric, ligand-gated cation channels with high calcium permeability among other activities. nAChRs are excitatory neurotrasnmitter receptors formed by a collection of nAChR subunits known to mediate synaptic transmission in the nervous system and the neuromuscular junction. Each nAchR subunit confers differential attributes to channel properties, including activation, deactivation and desensitization kinetics, pH sensitivity, cation permeability, and binding to allosteric modulators. CHRNA7 forms homopentameric neuronal acetylcholine receptors abundantly expressed in the central nervous system, characterized by fast desensitization and high calcium permeability. Also forms heteropentamers with CHRNB2, mainly expressed in basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Involved in the modulation of calcium-dependent signaling pathways and influences the release of neurotransmitters, including dopamine, glutamate and GABA. Also expressed in non-neuronal cells such as immune cells like lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages. In T cells, activation induces metabotropic signaling that results in an increase of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations, independent of ionotropic receptor functions. In macrophages, required for acetylcholine-mediated inhibition of TNF and other inflammatory cytokine release. Once activated by acetylcholine, nicotine or other agonists, selectively inhibits production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while leaving anti-inflammatory cytokines undisturbed. Stimulates the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, controlling inflammation by inhibiting NFKB nuclear translocation and activating the JAK2-STAT3 pathway, independently of ion channel activity. Also expressed in the urothelium where it modulates reflex bladder activity by increasing intracellular calcium through internal stores and decreasing basal ATP release. |
| Protein Name | Neuronal Acetylcholine Receptor Subunit Alpha-7Nachr7Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunit Alpha-7 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-629594 |
| Cellular Localisation | Postsynaptic Cell MembraneMulti-Pass Membrane ProteinCell MembraneTmem35a/Nacho Promotes Its Trafficking To The Cell MembraneRic3 Promotes Its Trafficking To The Cell Membrane |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Neuronal Acetylcholine Receptor Subunit Alpha-7 antibodyAnti-Nachr7 antibodyAnti-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subunit Alpha-7 antibodyAnti-CHRNA7 antibodyAnti-NACHRA7 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org

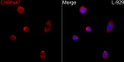
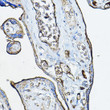
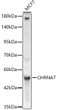





![Western blot analysis of lysates from wild type (WT) and Prion Protein knockout (KO) HeLa cells, using [KO Validated] Prion Protein Rabbit polyclonal antibody (STJ11100031) at 1:1000 dilution. Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (STJS000856) at 1:10000 dilution. Lysates/proteins: 25 Mu g per lane. Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST. Detection: ECL Basic Kit. Exposure time: 180s. Western blot analysis of lysates from wild type (WT) and Prion Protein knockout (KO) HeLa cells, using [KO Validated] Prion Protein Rabbit polyclonal antibody (STJ11100031) at 1:1000 dilution. Secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) (STJS000856) at 1:10000 dilution. Lysates/proteins: 25 Mu g per lane. Blocking buffer: 3% nonfat dry milk in TBST. Detection: ECL Basic Kit. Exposure time: 180s.](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-zso2xnchw9/images/stencil/600x533/products/89103/357560/STJ11100031_1__14868.1713121685.jpg?c=1)

