| Host: |
HEK293 cells |
| Reactivity: |
Mouse |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
Recombinant-Mouse IL-17F-C-His protein was developed from hek293 cells and has a target region of C-His. For use in research applications. |
| Formulation: |
Lyophilized from a 0.22 Mu m filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. Contact us for customized product form or formulation. |
| Immunoreactivity: |
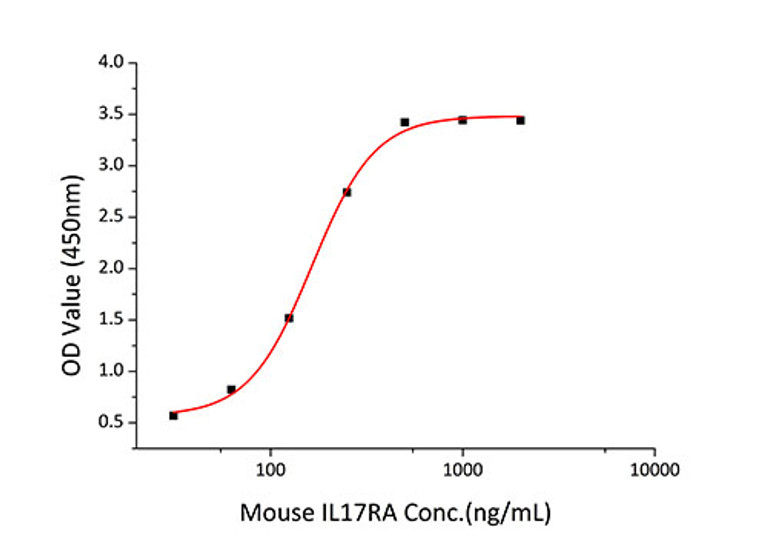
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized recombinant Mouse IL-17F at 2 Mu g/mL (100 Mu L/well) can bind recombinant Mouse IL17RA with a linear range of 31.25-163 ng/mL. |
| Gene Symbol: |
Il17f |
| Gene ID: |
257630 |
| Uniprot ID: |
IL17F_MOUSE |
| Immunogen Region: |
Met1-Ala161 |
| Immunogen: |
Recombinant Mouse IL-17F Protein is produced by HEK293 cells expression system. The target protein is expressed with sequence (Met1-Ala161) of mouse IL-17F (Accession #NP_665855.2) fused with a 6×His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Tissue Specificity | Expressed by T-helper 17 cells (Th17) (at protein level). The expression pattern reflects the differentiation state. In fully differentiated Th17 cells, IL17A-IL17F heterodimers are produced at higher levels than IL17A-IL17A and IL17F-IL17F dimers. Dominantly secreted in intestine. Expressed by resident cells of the lamina propria, both epithelial cells and immune cell subsets including natural killer cells, dendritic cells, macrophages and various T and B cell subsets. Expressed by epithelial cells and innate immune cells in the colon. Expressed in group 3 innate lymphoid cells. |
| Function | Effector cytokine of innate and adaptive immune system involved in antimicrobial host defense and maintenance of tissue integrity. IL17A-IL17F signals via IL17RA-IL17RC heterodimeric receptor complex, triggering homotypic interaction of IL17RA and IL17RC chains with TRAF3IP2 adapter through SEFIR domains. This leads to downstream TRAF6-mediated activation of NF-kappa-B and MAPkinase pathways ultimately resulting in transcriptional activation of cytokines, chemokines, antimicrobial peptides and matrix metalloproteinases, with potential strong immune inflammation. IL17A-IL17F is primarily involved in host defense against extracellular bacteria and fungi by inducing neutrophilic inflammation. As signature effector cytokine of T-helper 17 cells (Th17), primarily induces neutrophil activation and recruitment at infection and inflammatory sites. Stimulates the production of antimicrobial beta-defensins DEFB1, DEFB103A, and DEFB104A by mucosal epithelial cells, limiting the entry of microbes through the epithelial barriers. IL17F homodimer can signal via IL17RC homodimeric receptor complex, triggering downstream activation of TRAF6 and NF-kappa-B signaling pathway. Via IL17RC induces transcriptional activation of IL33, a potent cytokine that stimulates group 2 innate lymphoid cells and adaptive T-helper 2 cells involved in pulmonary allergic response to fungi. Likely via IL17RC, promotes sympathetic innervation of peripheral organs by coordinating the communication between gamma-delta T cells and parenchymal cells. Stimulates sympathetic innervation of thermogenic adipose tissue by driving TGFB1 expression. Regulates the composition of intestinal microbiota and immune tolerance by inducing antimicrobial proteins that specifically control the growth of commensal Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes. |
| Protein Name | Interleukin-17fIl-17f |
| Cellular Localisation | Secreted |
| Alternative Protein Names | Interleukin-17f proteinIl-17f proteinIl17f protein |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance