| Host: |
E. coli |
| Reactivity: |
Human |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
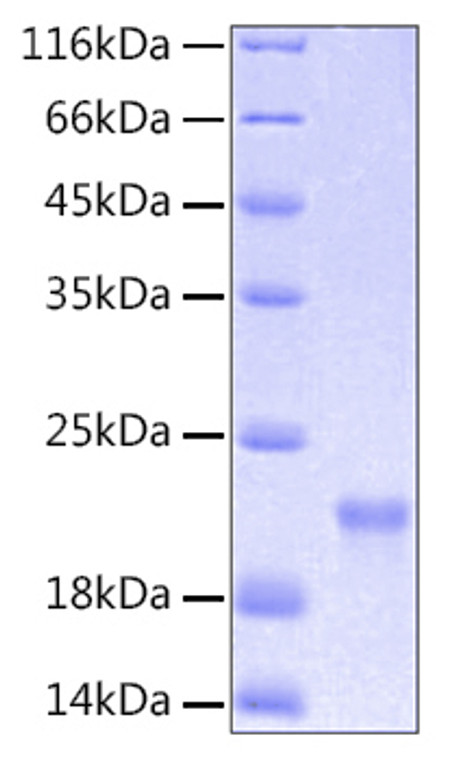
Recombinant-Human IL-6-C-His protein was developed from e. coli and has a target region of C-His. For use in research applications. |
| Formulation: |
Lyophilized from a 0.22 Mu m filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. Contact us for customized product form or formulation. |
| Immunoreactivity: |
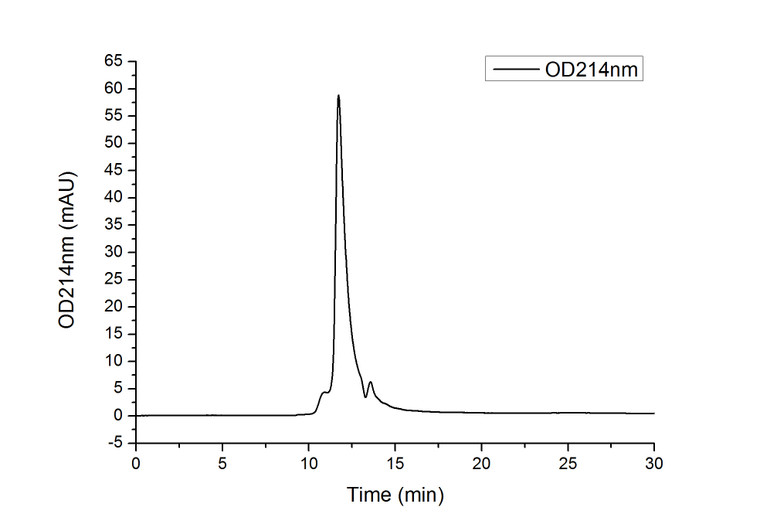
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Recombinant Human IL6R at 1 Mu g/mL (100 Mu L/well) can bind Recombinant Human IL-6 with a linear range of 20-70 ng/mL.2. Measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human eryth |
| Gene Symbol: |
IL6 |
| Gene ID: |
3569 |
| Uniprot ID: |
IL6_HUMAN |
| Immunogen Region: |
Pro29-Met212 |
| Immunogen: |
Recombinant Human IL-6 Protein is produced by E. coli expression system. The target protein is expressed with sequence (Pro29-Met212) of human IL6 (Accession #NP_000591.1) fused with an initial Met at the N-terminus and a 6×His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Tissue Specificity | Produced by skeletal muscle. |
| Post Translational Modifications | N- and O-glycosylated. |
| Function | Cytokine with a wide variety of biological functions in immunity, tissue regeneration, and metabolism. Binds to IL6R, then the complex associates to the signaling subunit IL6ST/gp130 to trigger the intracellular IL6-signaling pathway (Probable). The interaction with the membrane-bound IL6R and IL6ST stimulates 'classic signaling', whereas the binding of IL6 and soluble IL6R to IL6ST stimulates 'trans-signaling'. Alternatively, 'cluster signaling' occurs when membrane-bound IL6:IL6R complexes on transmitter cells activate IL6ST receptors on neighboring receiver cells (Probable). IL6 is a potent inducer of the acute phase response. Rapid production of IL6 contributes to host defense during infection and tissue injury, but excessive IL6 synthesis is involved in disease pathology. In the innate immune response, is synthesized by myeloid cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells, upon recognition of pathogens through toll-like receptors (TLRs) at the site of infection or tissue injury (Probable). In the adaptive immune response, is required for the differentiation of B cells into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Plays a major role in the differentiation of CD4(+) T cell subsets. Essential factor for the development of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells that are required for the induction of germinal-center formation. Required to drive naive CD4(+) T cells to the Th17 lineage. Also required for proliferation of myeloma cells and the survival of plasmablast cells. Acts as an essential factor in bone homeostasis and on vessels directly or indirectly by induction of VEGF, resulting in increased angiogenesis activity and vascular permeability. Induces, through 'trans-signaling' and synergistically with IL1B and TNF, the production of VEGF. Involved in metabolic controls, is discharged into the bloodstream after muscle contraction increasing lipolysis and improving insulin resistance. 'Trans-signaling' in central nervous system also regulates energy and glucose homeostasis. Mediates, through GLP-1, crosstalk between insulin-sensitive tissues, intestinal L cells and pancreatic islets to adapt to changes in insulin demand. Also acts as a myokine (Probable). Plays a protective role during liver injury, being required for maintenance of tissue regeneration. Also has a pivotal role in iron metabolism by regulating HAMP/hepcidin expression upon inflammation or bacterial infection. Through activation of IL6ST-YAP-NOTCH pathway, induces inflammation-induced epithelial regeneration. |
| Protein Name | Interleukin-6Il-6B-Cell Stimulatory Factor 2Bsf-2Ctl Differentiation FactorCdfHybridoma Growth FactorInterferon Beta-2Ifn-Beta-2 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-1059683Reactome: R-HSA-110056Reactome: R-HSA-112411Reactome: R-HSA-2559582Reactome: R-HSA-381426Reactome: R-HSA-6783783Reactome: R-HSA-6785807Reactome: R-HSA-8853884Reactome: R-HSA-8957275Reactome: R-HSA-9660821Reactome: R-HSA-9662834 |
| Cellular Localisation | Secreted |
| Alternative Protein Names | Interleukin-6 proteinIl-6 proteinB-Cell Stimulatory Factor 2 proteinBsf-2 proteinCtl Differentiation Factor proteinCdf proteinHybridoma Growth Factor proteinInterferon Beta-2 proteinIfn-Beta-2 proteinIL6 proteinIFNB2 protein |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance