| Applications: |
ELISA |
| Reactivity: |
Rat |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Sensitivity: |
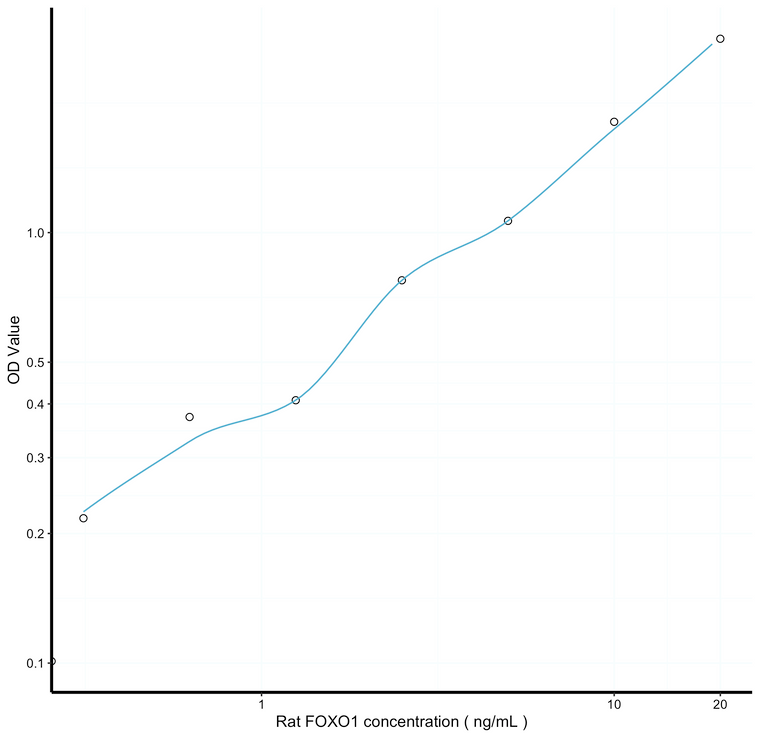
0.136ng/mL |
| Detection Limit: |
0.312-20ng/mL |
| Short Description: |
This FOXO1 Sandwich ELISA Kit is an in-vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the measurement of samples in rat cell culture supernatant, serum and plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin). |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store the unopened kit in the fridge at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. Once opened store individual kit contents according to components table provided with the kit. |
| Assay Time: |
4.5 hrs |
| Gene Symbol: |
Foxo1 |
| Gene ID: |
84482 |
| Uniprot ID: |
FOXO1_RAT |
| Sample Type: |
tissue homogenates, cell lysates or other biological fluids. |
| Tissue Specificity | |
| Post Translational Modifications | Phosphorylation by NLK promotes nuclear export and inhibits the transcriptional activity. In response to growth factors, phosphorylation on Thr-24, Ser-250 and Ser-313 by PKB/AKT1 promotes nuclear export and inactivation of transactivational activity. Phosphorylation on Thr-24 is required for binding 14-3-3 proteins. Phosphorylation of Ser-250 decreases DNA-binding activity and promotes the phosphorylation of Thr-24 and Ser-313, permitting phosphorylation of Ser-316 and Ser-319, probably by CDK1, leading to nuclear exclusion and loss of function. Stress signals, such as response to oxygen or nitric oxide, attenuate the PKB/AKT1-mediated phosphorylation leading to nuclear retention. Phosphorylation of Ser-323 is independent of IGF1 and leads to reduced function. Dephosphorylated on Thr-24 and Ser-250 by PP2A in beta-cells under oxidative stress leading to nuclear retention. Phosphorylation of Ser-243 by CDK1 disrupts binding of 14-3-3 proteins leading to nuclear accumulation and has no effect on DNA binding nor transcriptional activity. Phosphorylation by STK4/MST1 on Ser-206, upon oxidative stress, inhibits binding to 14-3-3 proteins and nuclear export. PPIA/CYPA promotes its dephosphorylation on Ser-250. Ubiquitinated by SKP2. Ubiquitination leads to proteasomal degradation. Methylation inhibits AKT1-mediated phosphorylation at Ser-250 and is increased by oxidative stress. Acetylation at Lys-256 and Lys-268 are necessary for autophagic cell death induction. Deacetylated by SIRT2 in response to oxidative stress or serum deprivation, thereby negatively regulating FOXO1-mediated autophagic cell death. Once in the nucleus, acetylated by CREBBP/EP300. Acetylation diminishes the interaction with target DNA and attenuates the transcriptional activity. It increases the phosphorylation at Ser-250. Deacetylation by SIRT1 results in reactivation of the transcriptional activity. Oxidative stress by hydrogen peroxide treatment appears to promote deacetylation and uncoupling of insulin-induced phosphorylation. By contrast, resveratrol acts independently of acetylation. Acetylated. Acetylation at Lys-256 and Lys-268 are necessary for autophagic cell death induction. Deacetylated by SIRT2 in response to oxidative stress or serum deprivation, thereby negatively regulating FOXO1-mediated autophagic cell death. Once in the nucleus, acetylated by CREBBP/EP300. Acetylation diminishes the interaction with target DNA and attenuates the transcriptional activity. It increases the phosphorylation at Ser-250. Deacetylation by SIRT1 results in reactivation of the transcriptional activity. Oxidative stress by hydrogen peroxide treatment appears to promote deacetylation and uncoupling of insulin-induced phosphorylation. By contrast, resveratrol acts independently of acetylation. Acetylated at Lys-417, promoting its localization to the nucleus and transcription factor activity. Deacetylation at Lys-417 by SIRT6, promotes its translocation into the cytoplasm, preventing its transcription factor activity. Deacetylation and subsequent inhibition by SIRT6 has different effects depending on cell types: it inhibits gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes, promotes glucose sensing in pancreatic beta-cells and regulates lipid catabolism in brown adipocytes. |
| Function | Transcription factor that is the main target of insulin signaling and regulates metabolic homeostasis in response to oxidative stress. Binds to the insulin response element (IRE) with consensus sequence 5'-TTG/ATTTTG-3' and the related Daf-16 family binding element (DBE) with consensus sequence 5'-TTG/ATTTAC-3'. Activity suppressed by insulin. Main regulator of redox balance and osteoblast numbers and controls bone mass. Orchestrates the endocrine function of the skeleton in regulating glucose metabolism. Also acts as a key regulator of chondrogenic commitment of skeletal progenitor cells in response to lipid availability: when lipids levels are low, translocates to the nucleus and promotes expression of SOX9, which induces chondrogenic commitment and suppresses fatty acid oxidation. Acts synergistically with ATF4 to suppress osteocalcin/BGLAP activity, increasing glucose levels and triggering glucose intolerance and insulin insensitivity. Also suppresses the transcriptional activity of RUNX2, an upstream activator of osteocalcin/BGLAP. Acts as an inhibitor of glucose sensing in pancreatic beta cells by acting as a transcription repressor and suppressing expression of PDX1. In hepatocytes, promotes gluconeogenesis by acting together with PPARGC1A and CEBPA to activate the expression of genes such as IGFBP1, G6PC1 and PCK1. Also promotes gluconeogenesis by directly promoting expression of PPARGC1A and G6PC1. Important regulator of cell death acting downstream of CDK1, PKB/AKT1 and STK4/MST1. Promotes neural cell death. Mediates insulin action on adipose tissue. Regulates the expression of adipogenic genes such as PPARG during preadipocyte differentiation and, adipocyte size and adipose tissue-specific gene expression in response to excessive calorie intake. Regulates the transcriptional activity of GADD45A and repair of nitric oxide-damaged DNA in beta-cells. Required for the autophagic cell death induction in response to starvation or oxidative stress in a transcription-independent manner. Mediates the function of MLIP in cardiomyocytes hypertrophy and cardiac remodeling. Regulates endothelial cell (EC) viability and apoptosis in a PPIA/CYPA-dependent manner via transcription of CCL2 and BCL2L11 which are involved in EC chemotaxis and apoptosis. |
| Protein Name | Forkhead Box Protein O1Forkhead Box Protein O1aForkhead In Rhabdomyosarcoma |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-RNO-198693Reactome: -RNO-211163Reactome: -RNO-5687128Reactome: -RNO-9614399Reactome: -RNO-9617629Reactome: -RNO-9617828 |
| Cellular Localisation | CytoplasmNucleusShuttles Between The Cytoplasm And NucleusLargely Nuclear In Unstimulated CellsIn OsteoblastsColocalizes With Atf4 And Runx2 In The NucleusSerum Deprivation Increases Localization To The NucleusLeading To Activate Expression Of Sox9 And Subsequent ChondrogenesisInsulin-Induced Phosphorylation At Ser-253 By Pkb/Akt1 LeadsVia Stimulation Of Thr-24 PhosphorylationTo Binding Of 14-3-3 Proteins And Nuclear Export To The Cytoplasm Where It Is Degraded By The Ubiquitin-Proteasomal PathwayPhosphorylation At Ser-249 By Cdk1 Disrupts Binding Of 14-3-3 Proteins And Promotes Nuclear AccumulationPhosphorylation By Nlk Results In Nuclear ExportTranslocates To The Nucleus Upon Oxidative Stress-Induced Phosphorylation At Ser-212 By Stk4/Mst1Sgk1-Mediated Phosphorylation Also Results In Nuclear TranslocationRetained In The Nucleus Under Stress Stimuli Including Oxidative StressNutrient Deprivation Or Nitric OxideMethylated Form Is NuclearPpia/Cypa Stimulates Its Nuclear AccumulationDeacetylation By Sirt6Promotes Its Translocation Into The Cytoplasm |
| Alternative ELISA Names | Forkhead Box Protein O1 ELISA kitForkhead Box Protein O1a ELISA kitForkhead In Rhabdomyosarcoma ELISA kitFoxo1 ELISA kitFoxo1a ELISA kit |
| output | |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance