| Applications: |
ELISA |
| Reactivity: |
Mouse |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Sensitivity: |
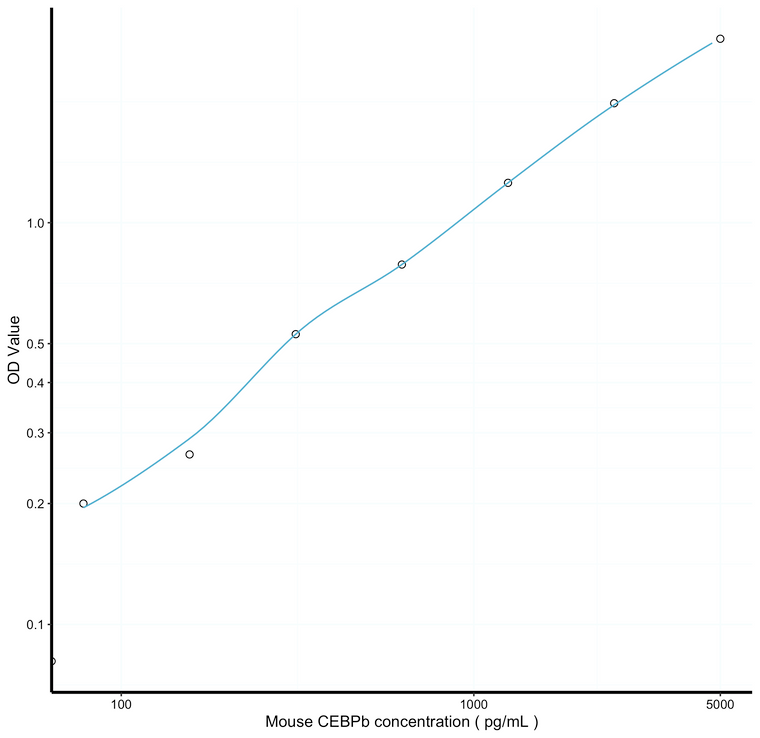
33pg/mL |
| Detection Limit: |
78.1-5000pg/mL |
| Short Description: |
This CEBPb Sandwich ELISA Kit is an in-vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the measurement of samples in mouse cell culture supernatant, serum and plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin). |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store the unopened kit in the fridge at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. Once opened store individual kit contents according to components table provided with the kit. |
| Assay Time: |
4.5 hrs |
| Gene Symbol: |
Cebpb |
| Gene ID: |
12608 |
| Uniprot ID: |
CEBPB_MOUSE |
| Sample Type: |
tissue homogenates, cell lysates or other biological fluids. |
| Tissue Specificity | Abundantly expressed in myoblasts. Enriched in brown adipose tissue (BAT) versus white adipose tissue (WAT). Expressed in hepatocytes (at protein level). Expressed in T lymphocytes. The expression in granulosa cells of antral follicles is induced by luteinizing hormone. Expressed in chondrocytes and osteoblasts (at protein level). |
| Post Translational Modifications | Sumoylated by polymeric chains of SUMO2 or SUMO3. Sumoylation at Lys-133 is required for inhibition of T-cells proliferation. In adipocytes, sumoylation at Lys-133 by PIAS1 leads to ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Desumoylated by SENP2, which abolishes ubiquitination and stabilizes protein levels. Ubiquitinated, leading to proteasomal degradation. Phosphorylated at Thr-188 by MAPK and CDK2, serves to prime phosphorylation at Thr-179 and Ser-184 by GSK3B and acquire DNA-binding as well as transactivation activities, required to induce adipogenesis. MAPK and CDK2 act sequentially to maintain Thr-188 in the primed phosphorylated state during mitotical cloning expansion and thereby progression of terminal differentiation. Phosphorylation at Thr-217 enhances transactivation activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-276 in response to calcium increases transactivation activity. Phosphorylated at Thr-188 by RPS6KA1. O-glycosylated, glycosylation at Ser-180 and Ser-181 prevents phosphorylation on Thr-188, Ser-184 and Thr-179 and DNA binding activity which delays the adipocyte differentiation program. Acetylated. Acetylation at Lys-39 is an important and dynamic regulatory event that contributes to its ability to transactivate target genes, including those associated with adipogenesis and adipocyte function. Deacetylation by HDAC1 represses its transactivation activity. Acetylated by KAT2A and KAT2B within a cluster of lysine residues between amino acids 98-102, this acetylation is strongly induced by glucocorticoid treatment and enhances transactivation activity. Methylated. Methylation at Arg-3 by CARM1 and at Lys-39 by EHMT2, inhibits transactivation activity. Methylation is probably inhibited by phosphorylation at Thr-188. |
| Function | Important transcription factor regulating the expression of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses. Also plays a significant role in adipogenesis, as well as in the gluconeogenic pathway, liver regeneration, and hematopoiesis. The consensus recognition site is 5'-TTGNNGNAATG-3'. Its functional capacity is governed by protein interactions and post-translational protein modifications. During early embryogenesis, plays essential and redundant roles with CEBPA. Has a promitotic effect on many cell types such as hepatocytes and adipocytes but has an antiproliferative effect on T-cells by repressing MYC expression, facilitating differentiation along the T-helper 2 lineage. Binds to regulatory regions of several acute-phase and cytokines genes and plays a role in the regulation of acute-phase reaction and inflammation. Also plays a role in intracellular bacteria killing. During adipogenesis, is rapidly expressed and, after activation by phosphorylation, induces CEBPA and PPARG, which turn on the series of adipocyte genes that give rise to the adipocyte phenotype. The delayed transactivation of the CEBPA and PPARG genes by CEBPB appears necessary to allow mitotic clonal expansion and thereby progression of terminal differentiation. Essential for female reproduction because of a critical role in ovarian follicle development. Restricts osteoclastogenesis. Together with NFE2L1.represses expression of DSPP during odontoblast differentiation. Isoform 2: Essential for gene expression induction in activated macrophages. Plays a major role in immune responses such as CD4(+) T-cell response, granuloma formation and endotoxin shock. Not essential for intracellular bacteria killing. Isoform 3: Acts as a dominant negative through heterodimerization with isoform 2. Promotes osteoblast differentiation and osteoclastogenesis. |
| Protein Name | Ccaat/Enhancer-Binding Protein BetaC/Ebp BetaAgp/EbpInterleukin-6-Dependent-Binding ProteinIl-6dbpLiver-Enriched Transcriptional ActivatorLap |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-MMU-2559582 |
| Cellular Localisation | NucleusCytoplasmIn T-Cells When Sumoylated Drawn To Pericentric Heterochromatin Thereby Allowing ProliferationTranslocates To The Nucleus When Phosphorylated At Ser-288 |
| Alternative ELISA Names | Ccaat/Enhancer-Binding Protein Beta ELISA kitC/Ebp Beta ELISA kitAgp/Ebp ELISA kitInterleukin-6-Dependent-Binding Protein ELISA kitIl-6dbp ELISA kitLiver-Enriched Transcriptional Activator ELISA kitLap ELISA kitCebpb ELISA kit |
| output | |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance