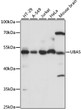
| Tissue Specificity | Widely expressed. |
| Function | E1-like enzyme which specifically catalyzes the first step in ufmylation. Activates UFM1 by first adenylating its C-terminal glycine residue with ATP, and thereafter linking this residue to the side chain of a cysteine residue in E1, yielding a UFM1-E1 thioester and free AMP. Activates UFM1 via a trans-binding mechanism, in which UFM1 interacts with distinct sites in both subunits of the UBA5 homodimer. Trans-binding also promotes stabilization of the UBA5 homodimer, and enhances ATP-binding. Transfer of UFM1 from UBA5 to the E2-like enzyme UFC1 also takes place using a trans mechanism. Ufmylation plays a key role in various processes, such as ribosome recycling, response to DNA damage, interferon response or reticulophagy (also called ER-phagy). Ufmylation is essential for erythroid differentiation of both megakaryocytes and erythrocytes. |
| Protein Name | Ubiquitin-Like Modifier-Activating Enzyme 5Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme 5Thifp1Ufm1-Activating EnzymeUbiquitin-Activating Enzyme E1 Domain-Containing Protein 1 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-983168 |
| Cellular Localisation | CytoplasmNucleusEndoplasmic Reticulum MembraneGolgi ApparatusLocalizes Mainly In The CytoplasmWhile It Localizes To The Nucleus In Presence Of Sumo2Interaction With Gabarapl2 Promotes Localization To The Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Ubiquitin-Like Modifier-Activating Enzyme 5 antibodyAnti-Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme 5 antibodyAnti-Thifp1 antibodyAnti-Ufm1-Activating Enzyme antibodyAnti-Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme E1 Domain-Containing Protein 1 antibodyAnti-UBA5 antibodyAnti-UBE1DC1 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org