| Host: |
Goat |
| Applications: |
WB |
| Reactivity: |
Human/Rat/Mouse/Monkey/Canine |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
Goat polyclonal antibody anti-Hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor) (780aa C-Term) is suitable for use in Western Blot research applications. |
| Clonality: |
Polyclonal |
| Conjugation: |
Unconjugated |
| Isotype: |
IgG |
| Formulation: |
PBS, 20% Glycerol and 0.05% Sodium Azide. |
| Purification: |
This antibody is epitope-affinity purified from goat antiserum. |
| Concentration: |
3 mg/mL |
| Dilution Range: |
WB 1:500-1:2000Ferreira JV Soares AR Ramalho J et al. Sci Adv 2022 Mar PMID: 35333565Martins F Sacramento JF Olea E et al. Antioxidants-Basel 2021 Aug PMID: 34439481Ferreira JV Rosa Soares A Ramalho JS et al. PLoS One. 2019 Oct. PMID: |
| Storage Instruction: |
For continuous use, store at 2-8 C for one-two days. For extended storage, store in-20 C freezer. Working dilution samples should be discarded if not used within 12 hours. |
| Gene Symbol: |
HIF1A |
| Gene ID: |
3091 |
| Uniprot ID: |
HIF1A_HUMAN |
| Immunogen Region: |
780aa C-Term |
| Accession Number: |
ENSG00000100644 |
| Specificity: |
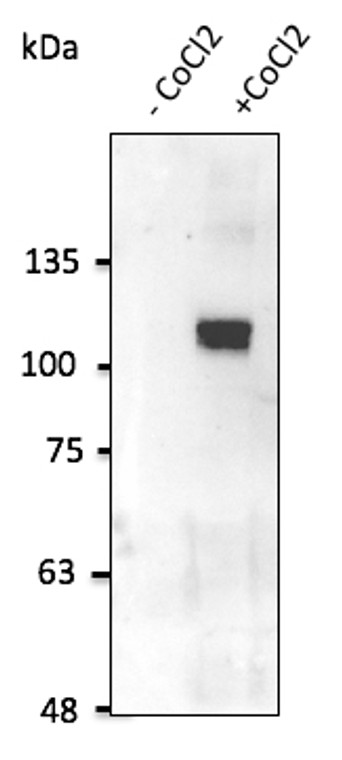
Detects HIF1a in transfected cells and a band of approximately 120 kDa by Western blot in cell lysates. |
| Immunogen: |
Purified recombinant peptide derived from within residues 780 aa to the C-terminus of human HIF1a produced in E. coli. |
| Immunogen Sequence: |
LLGQSMDESGLPQLTSYDCE VNAPIQGSRNLLQGEELLRA LDQVN |
| Tissue Specificity | Expressed in most tissues with highest levels in kidney and heart. Overexpressed in the majority of common human cancers and their metastases, due to the presence of intratumoral hypoxia and as a result of mutations in genes encoding oncoproteins and tumor suppressors. A higher level expression seen in pituitary tumors as compared to the pituitary gland. |
| Post Translational Modifications | S-nitrosylation of Cys-800 may be responsible for increased recruitment of p300 coactivator necessary for transcriptional activity of HIF-1 complex. Requires phosphorylation for DNA-binding. Phosphorylation at Ser-247 by CSNK1D/CK1 represses kinase activity and impairs ARNT binding. Phosphorylation by GSK3-beta and PLK3 promote degradation by the proteasome. Sumoylated.with SUMO1 under hypoxia. Sumoylation is enhanced through interaction with RWDD3. Both sumoylation and desumoylation seem to be involved in the regulation of its stability during hypoxia. Sumoylation can promote either its stabilization or its VHL-dependent degradation by promoting hydroxyproline-independent HIF1A-VHL complex binding, thus leading to HIF1A ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Desumoylation by SENP1 increases its stability amd transcriptional activity. There is a disaccord between various publications on the effect of sumoylation and desumoylation on its stability and transcriptional activity (Probable). Acetylation of Lys-532 by ARD1 increases interaction with VHL and stimulates subsequent proteasomal degradation. Deacetylation of Lys-709 by SIRT2 increases its interaction with and hydroxylation by EGLN1 thereby inactivating HIF1A activity by inducing its proteasomal degradation. Polyubiquitinated.in normoxia, following hydroxylation and interaction with VHL. Lys-532 appears to be the principal site of ubiquitination. Clioquinol, the Cu/Zn-chelator, inhibits ubiquitination through preventing hydroxylation at Asn-803. Ubiquitinated by E3 ligase VHL. Deubiquitinated by UCHL1. In normoxia, is hydroxylated on Pro-402 and Pro-564 in the oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODD) by EGLN1/PHD2 and EGLN2/PHD1. EGLN3/PHD3 has also been shown to hydroxylate Pro-564. The hydroxylated prolines promote interaction with VHL, initiating rapid ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Deubiquitinated by USP20. Under hypoxia, proline hydroxylation is impaired and ubiquitination is attenuated, resulting in stabilization. In normoxia, is hydroxylated on Asn-803 by HIF1AN, thus abrogating interaction with CREBBP and EP300 and preventing transcriptional activation. This hydroxylation is inhibited by the Cu/Zn-chelator, Clioquinol. Repressed by iron ion, via Fe(2+) prolyl hydroxylase (PHD) enzymes-mediated hydroxylation and subsequent proteasomal degradation. The iron and 2-oxoglutarate dependent 3-hydroxylation of asparagine is (S) stereospecific within HIF CTAD domains. (Microbial infection) Glycosylated at Arg-18 by enteropathogenic E.coli protein NleB1: arginine GlcNAcylation enhances transcription factor activity and impairs glucose metabolism. |
| Function | Functions as a master transcriptional regulator of the adaptive response to hypoxia. Under hypoxic conditions, activates the transcription of over 40 genes, including erythropoietin, glucose transporters, glycolytic enzymes, vascular endothelial growth factor, HILPDA, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia. Plays an essential role in embryonic vascularization, tumor angiogenesis and pathophysiology of ischemic disease. Heterodimerizes with ARNT.heterodimer binds to core DNA sequence 5'-TACGTG-3' within the hypoxia response element (HRE) of target gene promoters. Activation requires recruitment of transcriptional coactivators such as CREBBP and EP300. Activity is enhanced by interaction with NCOA1 and/or NCOA2. Interaction with redox regulatory protein APEX1 seems to activate CTAD and potentiates activation by NCOA1 and CREBBP. Involved in the axonal distribution and transport of mitochondria in neurons during hypoxia. (Microbial infection) Upon infection by human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, is required for induction of glycolysis in monocytes and the consequent pro-inflammatory state. In monocytes, induces expression of ACE2 and cytokines such as IL1B, TNF, IL6, and interferons. Promotes human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 replication and monocyte inflammatory response. |
| Protein Name | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-AlphaHif-1-AlphaHif1-AlphaArnt-Interacting ProteinBasic-Helix-Loop-Helix-Pas Protein Mop1Class E Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein 78Bhlhe78Member Of Pas Protein 1Pas Domain-Containing Protein 8 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-1234158Reactome: R-HSA-1234174Reactome: R-HSA-1234176Reactome: R-HSA-2122947Reactome: R-HSA-400253Reactome: R-HSA-5689880Reactome: R-HSA-6785807Reactome: R-HSA-8849473Reactome: R-HSA-8857538Reactome: R-HSA-8951664Reactome: R-HSA-9701898 |
| Cellular Localisation | CytoplasmNucleusNucleus SpeckleColocalizes With Hif3a In The Nucleus And SpecklesCytoplasmic In NormoxiaNuclear Translocation In Response To Hypoxia |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha antibodyAnti-Hif-1-Alpha antibodyAnti-Hif1-Alpha antibodyAnti-Arnt-Interacting Protein antibodyAnti-Basic-Helix-Loop-Helix-Pas Protein Mop1 antibodyAnti-Class E Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein 78 antibodyAnti-Bhlhe78 antibodyAnti-Member Of Pas Protein 1 antibodyAnti-Pas Domain-Containing Protein 8 antibodyAnti-HIF1A antibodyAnti-BHLHE78 antibodyAnti-MOP1 antibodyAnti-PASD8 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance