| Applications: |
ELISA |
| Reactivity: |
Human |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Sensitivity: |
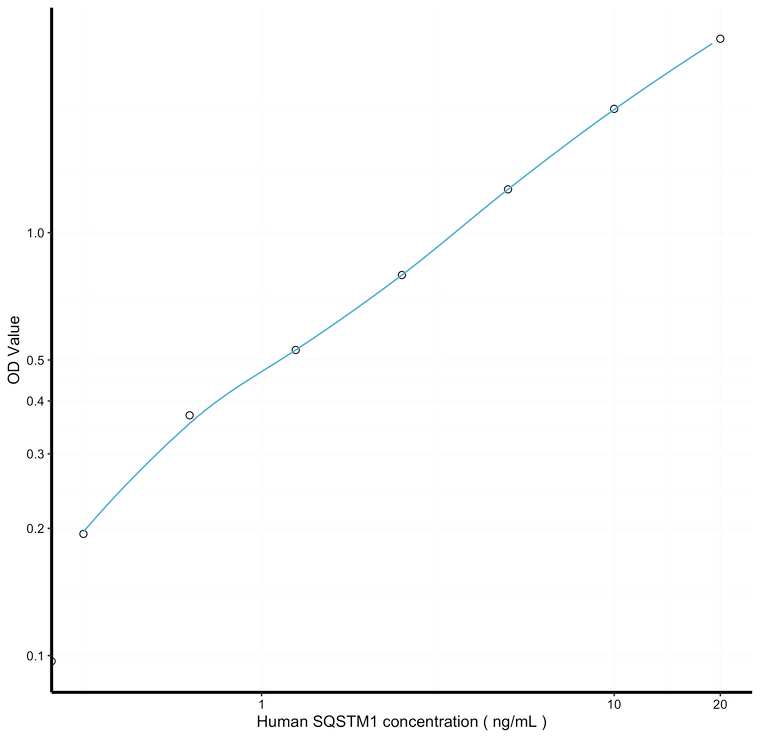
0.125ng/mL |
| Detection Limit: |
0.312-20ng/mL |
| Short Description: |
This SQSTM1 Sandwich ELISA Kit is an in-vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the measurement of samples in human cell culture supernatant, serum and plasma (EDTA, citrate, heparin). |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store the unopened kit in the fridge at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. Once opened store individual kit contents according to components table provided with the kit. |
| Assay Time: |
4.5 hrs |
| Gene Symbol: |
SQSTM1 |
| Gene ID: |
8878 |
| Uniprot ID: |
SQSTM_HUMAN |
| Sample Type: |
tissue homogenates, cell lysates or other biological fluids. |
| Tissue Specificity | Ubiquitously expressed. |
| Post Translational Modifications | Phosphorylated. May be phosphorylated by PRKCZ. Phosphorylated in vitro by TTN. Phosphorylation at Ser-403 by ULK1 is stimulated by SESN2. Phosphorylated at Ser-403 by TBK1, leading to promote relocalization of 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitinated STING1 to autophagosomes. Phosphorylation at Ser-349 by MTOR promotes interaction with KEAP1 and inactivation of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, promoting NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and expression of phase II detoxifying enzymes. Ubiquitinated by UBE2J1 and RNF26 at Lys-435: ubiquitinated SQSTM1 attracts specific vesicle-associated adapters, forming a molecular bridge that restrains cognate vesicles in the perinuclear region and organizes the endosomal pathway for efficient cargo transport. Deubiquitination by USP15 releases target vesicles for fast transport into the cell periphery. Ubiquitinated by the BCR(KEAP1) complex at Lys-420, increasing SQSTM1 sequestering activity and promoting its degradation. Ubiquitinated via 'Lys-29' and 'Lys-33'-linked polyubiquitination leading to xenophagic targeting of bacteria and inhibition of their replication. (Microbial infection) Cleaved by S.pyogenes SpeB protease.leading to its degradation. Degradation by SpeB prevents autophagy, promoting to S.pyogenes intracellular replication. (Microbial infection) Deubiquitinated by Epstein-Barr virus BPLF1.leading to inhibition of the recruitment of MAP1LC3A/LC3 to SQSTM1-positive structures. |
| Function | Autophagy receptor required for selective macroautophagy (aggrephagy). Functions as a bridge between polyubiquitinated cargo and autophagosomes. Interacts directly with both the cargo to become degraded and an autophagy modifier of the MAP1 LC3 family. Along with WDFY3, involved in the formation and autophagic degradation of cytoplasmic ubiquitin-containing inclusions (p62 bodies, ALIS/aggresome-like induced structures). Along with WDFY3, required to recruit ubiquitinated proteins to PML bodies in the nucleus. Also involved in autophagy of peroxisomes (pexophagy) in response to reactive oxygen species (ROS) by acting as a bridge between ubiquitinated PEX5 receptor and autophagosomes. May regulate the activation of NFKB1 by TNF-alpha, nerve growth factor (NGF) and interleukin-1. May play a role in titin/TTN downstream signaling in muscle cells. May regulate signaling cascades through ubiquitination. Adapter that mediates the interaction between TRAF6 and CYLD. May be involved in cell differentiation, apoptosis, immune response and regulation of K(+) channels. Involved in endosome organization by retaining vesicles in the perinuclear cloud: following ubiquitination by RNF26, attracts specific vesicle-associated adapters, forming a molecular bridge that restrains cognate vesicles in the perinuclear region and organizes the endosomal pathway for efficient cargo transport. Promotes relocalization of 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitinated STING1 to autophagosomes. Acts as an activator of the NFE2L2/NRF2 pathway via interaction with KEAP1: interaction inactivates the BCR(KEAP1) complex, promoting nuclear accumulation of NFE2L2/NRF2 and subsequent expression of cytoprotective genes. Sequesters tensin TNS2 into cytoplasmic puncta, promoting TNS2 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. |
| Protein Name | Sequestosome-1Ebi3-Associated Protein Of 60 KdaEbiapP60Phosphotyrosine-Independent Ligand For The Lck Sh2 Domain Of 62 KdaUbiquitin-Binding Protein P62 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-205043Reactome: R-HSA-209543Reactome: R-HSA-209560Reactome: R-HSA-5205685Reactome: R-HSA-8951664Reactome: R-HSA-9020702Reactome: R-HSA-9664873Reactome: R-HSA-9725370Reactome: R-HSA-9755511Reactome: R-HSA-9759194 |
| Cellular Localisation | CytoplasmCytosolPreautophagosomal StructureLate EndosomeLysosomeCytoplasmic VesicleAutophagosomeNucleusEndoplasmic ReticulumPml BodyMyofibrilSarcomereIn Cardiac MuscleLocalizes To The Sarcomeric BandCommonly Found In Inclusion Bodies Containing Polyubiquitinated Protein AggregatesIn Neurodegenerative DiseasesDetected In Lewy Bodies In Parkinson DiseaseNeurofibrillary Tangles In Alzheimer DiseaseAnd Htt Aggregates In Huntington DiseaseIn Protein Aggregate Diseases Of The LiverFound In Large Amounts In Mallory Bodies Of Alcoholic And Nonalcoholic SteatohepatitisHyaline Bodies In Hepatocellular CarcinomaAnd In Serpina1 AggregatesEnriched In Rosenthal Fibers Of Pilocytic AstrocytomaIn The CytoplasmObserved In Both Membrane-Free Ubiquitin-Containing Protein Aggregates (Sequestosomes) And Membrane-Surrounded AutophagosomesColocalizes With Trim13 In The Perinuclear Endoplasmic ReticulumCo-Localizes With Trim5 In Cytoplasmic BodiesWhen Nuclear Export Is Blocked By Treatment With Leptomycin BAccumulates In Pml Bodies |
| Alternative ELISA Names | Sequestosome-1 ELISA kitEbi3-Associated Protein Of 60 Kda ELISA kitEbiap ELISA kitP60 ELISA kitPhosphotyrosine-Independent Ligand For The Lck Sh2 Domain Of 62 Kda ELISA kitUbiquitin-Binding Protein P62 ELISA kitSQSTM1 ELISA kitORCA ELISA kitOSIL ELISA kit |
| output | |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance