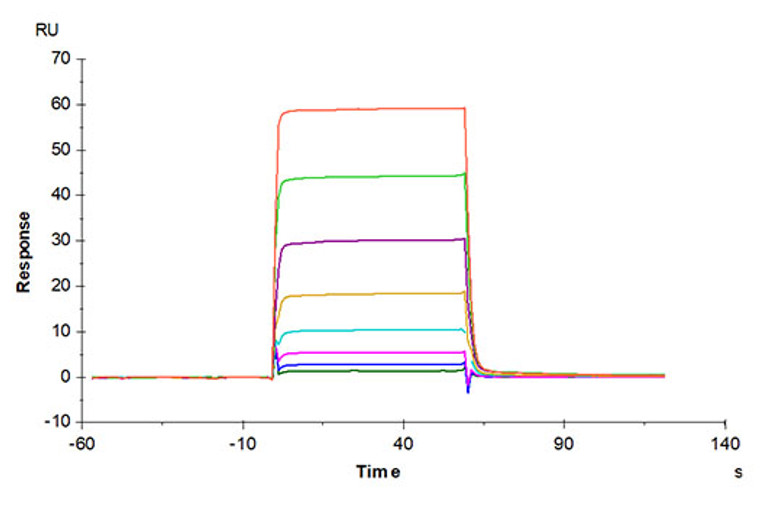
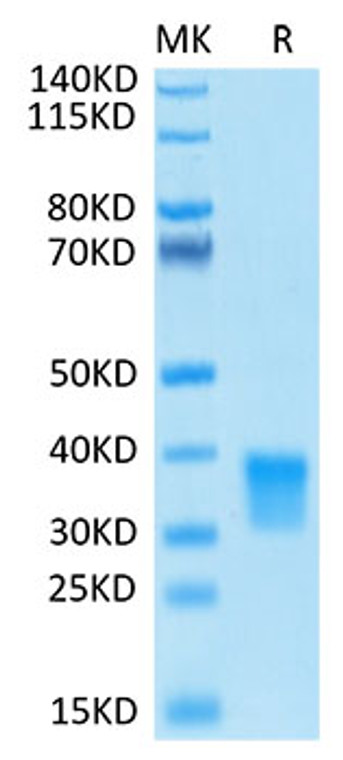
| Host: |
HEK293 cells |
| Reactivity: |
Human |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
Recombinant-Human Oncostatin-M/OSM-C-His & Avi protein was developed from hek293 cells and has a target region of C-His & Avi. For use in research applications. |
| Conjugation: |
Biotin |
| Formulation: |
Lyophilized from a 0.22 Mu m filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Gene Symbol: |
OSM |
| Gene ID: |
5008 |
| Uniprot ID: |
ONCM_HUMAN |
| Immunogen Region: |
Ala26-Arg221 |
| Immunogen: |
Biotinylated Recombinant Human Oncostatin M Protein is produced by Expi293 expression system. The target protein is expressed with sequence (Ala26-Arg221) of Human Oncostatin M fused with His tag and Avi tag at the C-terminal. |
| Function | Growth regulator. Inhibits the proliferation of a number of tumor cell lines. Stimulates proliferation of AIDS-KS cells. It regulates cytokine production, including IL-6, G-CSF and GM-CSF from endothelial cells. Uses both type I OSM receptor (heterodimers composed of LIFR and IL6ST) and type II OSM receptor (heterodimers composed of OSMR and IL6ST). Involved in the maturation of fetal hepatocytes, thereby promoting liver development and regeneration. |
| Protein Name | Oncostatin-MOsm |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-6785807Reactome: R-HSA-6788467 |
| Cellular Localisation | Secreted |
| Alternative Protein Names | Oncostatin-M proteinOsm proteinOSM protein |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance