| Host: |
HEK293 cells |
| Reactivity: |
Human |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
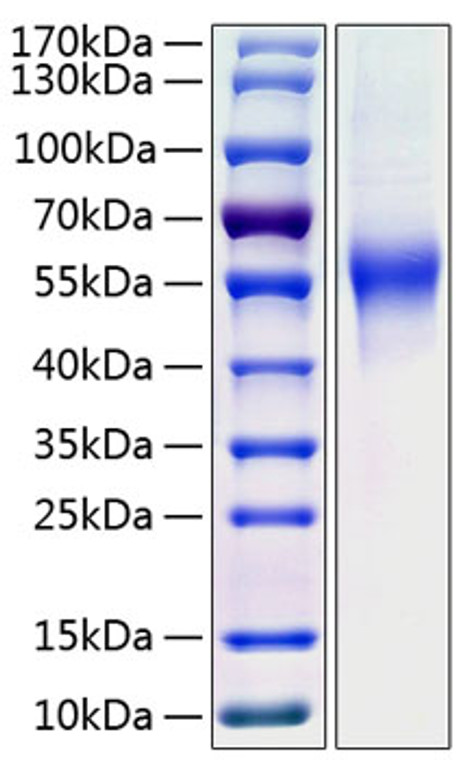
Recombinant-Human CD46-C-His protein was developed from hek293 cells and has a target region of C-His. For use in research applications. |
| Formulation: |
Lyophilized from a 0.22 Mu m filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. Contact us for customized product form or formulation. |
| Gene Symbol: |
CD46 |
| Gene ID: |
4179 |
| Uniprot ID: |
MCP_HUMAN |
| Immunogen Region: |
Cys35-Asp328 |
| Immunogen: |
Recombinant Human CD46 Protein is produced by HEK293 cells expression system. The target protein is expressed with sequence (Cys35-Asp328) of human CD46 (Accession #NP_758861.1) fused with a 6×His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Tissue Specificity | Expressed by all cells except erythrocytes. |
| Post Translational Modifications | N-glycosylated on Asn-83.Asn-114 and Asn-273 in most tissues, but probably less N-glycosylated in testis. N-glycosylation on Asn-114 and Asn-273 is required for cytoprotective function. N-glycosylation on Asn-114 is required for Measles virus binding. N-glycosylation on Asn-273 is required for Neisseria binding. N-glycosylation is not required for human adenovirus binding. Extensively O-glycosylated in the Ser/Thr-rich domain. O-glycosylation is required for Neisseria binding but not for Measles virus or human adenovirus binding. In epithelial cells, isoforms B/D/F/H/J/L/3 are phosphorylated by YES1 in response to infection by Neisseria gonorrhoeae.which promotes infectivity. In T-cells, these isoforms may be phosphorylated by LCK. |
| Function | Acts as a cofactor for complement factor I, a serine protease which protects autologous cells against complement-mediated injury by cleaving C3b and C4b deposited on host tissue. May be involved in the fusion of the spermatozoa with the oocyte during fertilization. Also acts as a costimulatory factor for T-cells which induces the differentiation of CD4+ into T-regulatory 1 cells. T-regulatory 1 cells suppress immune responses by secreting interleukin-10, and therefore are thought to prevent autoimmunity. (Microbial infection) A number of viral and bacterial pathogens seem to bind MCP in order to exploit its immune regulation property and directly induce an immunosuppressive phenotype in T-cells. (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Adenovirus subgroup B2 and Ad3. (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for cultured Measles virus. (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for Herpesvirus 6/HHV-6. (Microbial infection) May act as a receptor for pathogenic bacteria Neisseria and Streptococcus pyogenes. |
| Protein Name | Membrane Cofactor ProteinTlxTrophoblast Leukocyte Common AntigenCd Antigen Cd46 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-977606 |
| Cellular Localisation | Cytoplasmic VesicleSecretory VesicleAcrosome Inner MembraneSingle-Pass Type I Membrane ProteinInner Acrosomal Membrane Of SpermatozoaInternalized Upon Binding Of Measles VirusHerpesvirus 6 Or Neisseria GonorrhoeaeWhich Results In An Increased Susceptibility Of Infected Cells To Complement-Mediated InjuryIn Cancer Cells Or Cells Infected By NeisseriaShedding Leads To A Soluble Peptide |
| Alternative Protein Names | Membrane Cofactor Protein proteinTlx proteinTrophoblast Leukocyte Common Antigen proteinCd Antigen Cd46 proteinCD46 proteinMCP proteinMIC10 protein |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance