| Host: |
Rabbit |
| Applications: |
WB/IHC/IF |
| Reactivity: |
Human/Mouse/Rat/Monkey |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
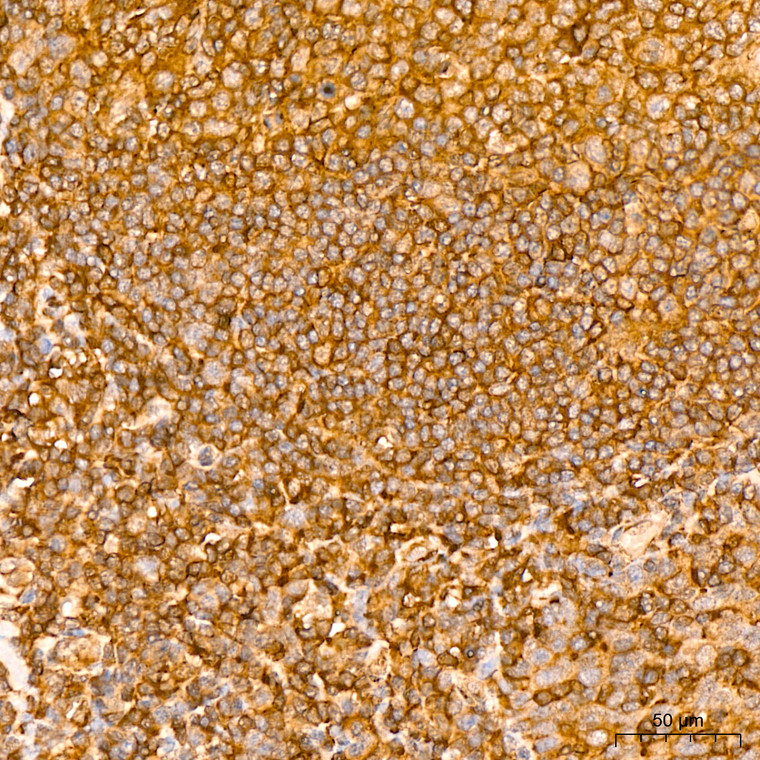
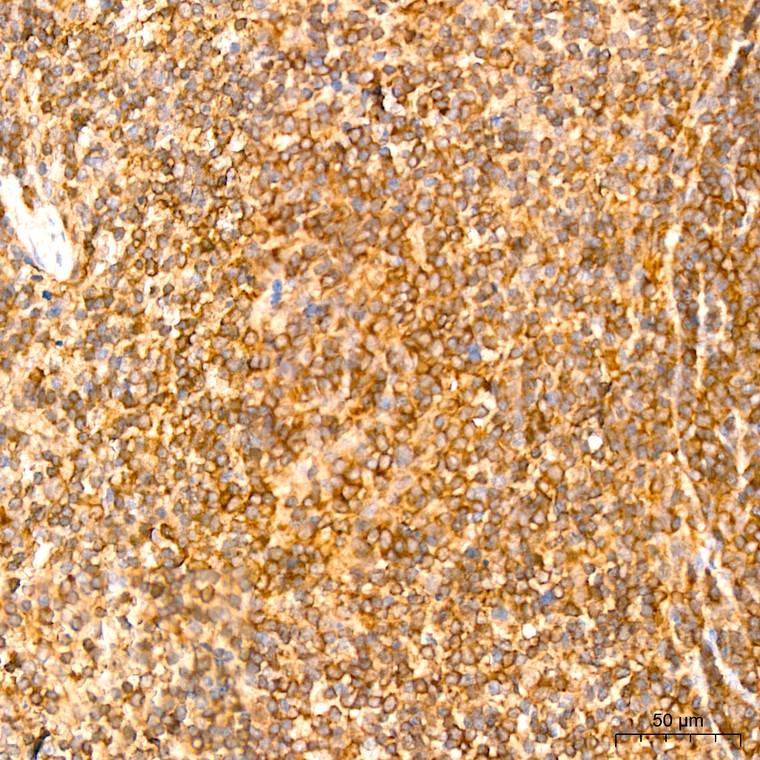
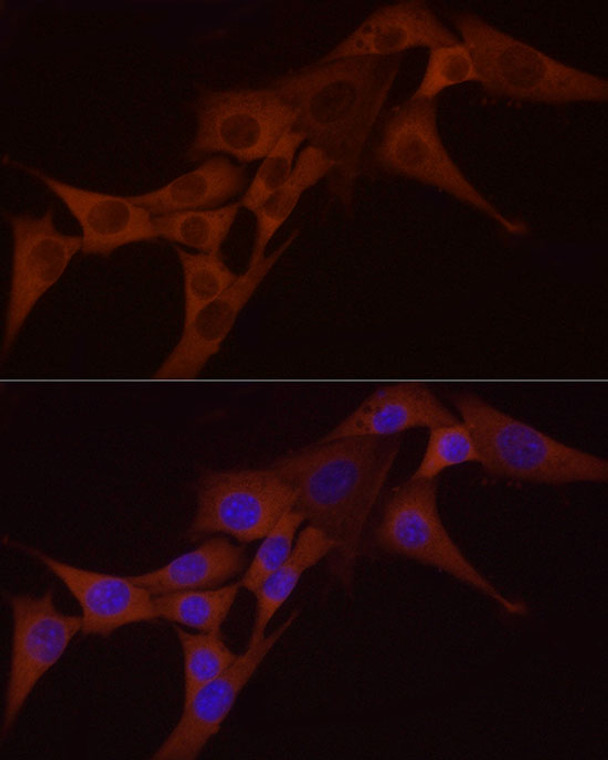
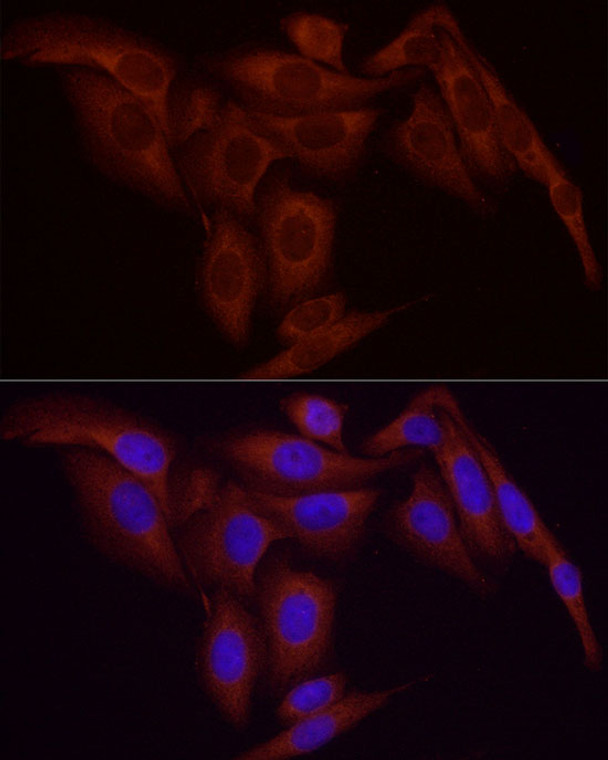
Rabbit monoclonal antibody anti-NF-kB p65 (450-551) is suitable for use in Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence research applications. |
| Clonality: |
Monoclonal |
| Clone ID: |
S8MR |
| Conjugation: |
Unconjugated |
| Isotype: |
IgG |
| Formulation: |
PBS with 0.05% Proclin300, 0.05% BSA, 50% Glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Purification: |
Affinity purification |
| Dilution Range: |
WB 1:500-1:1000IHC-P 1:500-1:1000IF/ICC 1:50-1:200ChIP 1:50-1:200 |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Gene Symbol: |
RELA |
| Gene ID: |
5970 |
| Uniprot ID: |
TF65_HUMAN |
| Immunogen Region: |
450-551 |
| Immunogen: |
A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 450-551 of human NF-Kappa B p65 (Q04206). |
| Immunogen Sequence: |
LGALLGNSTDPAVFTDLASV DNSEFQQLLNQGIPVAPHTT EPMLMEYPEAITRLVTGAQR PPDPAPAPLGAPGLPNGLLS GDEDFSSIADMDFSALLSQI SS |
| Post Translational Modifications | Ubiquitinated by RNF182, leading to its proteasomal degradation. Degradation is required for termination of NF-kappa-B response. Polyubiquitinated via 'Lys-29'-linked ubiquitin.leading to lysosomal degradation. Monomethylated at Lys-310 by SETD6. Monomethylation at Lys-310 is recognized by the ANK repeats of EHMT1 and promotes the formation of repressed chromatin at target genes, leading to down-regulation of NF-kappa-B transcription factor activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-311 disrupts the interaction with EHMT1 without preventing monomethylation at Lys-310 and relieves the repression of target genes. Phosphorylation at Ser-311 disrupts the interaction with EHMT1 and promotes transcription factor activity. Phosphorylation on Ser-536 stimulates acetylation on Lys-310 and interaction with CBP.the phosphorylated and acetylated forms show enhanced transcriptional activity. Phosphorylation at Ser-276 by RPS6KA4 and RPS6KA5 promotes its transactivation and transcriptional activities. Phosphorylation at Ser-75 by herpes simplex virus 1/HHV-1 inhibits NF-kappa-B activation. Reversibly acetylated.the acetylation seems to be mediated by CBP, the deacetylation by HDAC3 and SIRT2. Acetylation at Lys-122 enhances DNA binding and impairs association with NFKBIA. Acetylation at Lys-310 is required for full transcriptional activity in the absence of effects on DNA binding and NFKBIA association. Acetylation at Lys-310 promotes interaction with BRD4. Acetylation can also lower DNA-binding and results in nuclear export. Interaction with BRMS1 promotes deacetylation of Lys-310. Lys-310 is deacetylated by SIRT2. S-nitrosylation of Cys-38 inactivates the enzyme activity. Sulfhydration at Cys-38 mediates the anti-apoptotic activity by promoting the interaction with RPS3 and activating the transcription factor activity. Sumoylation by PIAS3 negatively regulates DNA-bound activated NF-kappa-B. Proteolytically cleaved within a conserved N-terminus region required for base-specific contact with DNA in a CPEN1-mediated manner, and hence inhibits NF-kappa-B transcriptional activity. |
| Function | NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor present in almost all cell types and is the endpoint of a series of signal transduction events that are initiated by a vast array of stimuli related to many biological processes such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The heterodimeric RELA-NFKB1 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. The NF-kappa-B heterodimeric RELA-NFKB1 and RELA-REL complexes, for instance, function as transcriptional activators. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. The inhibitory effect of I-kappa-B on NF-kappa-B through retention in the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with RELA. RELA shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappa-B complex. Beside its activity as a direct transcriptional activator, it is also able to modulate promoters accessibility to transcription factors and thereby indirectly regulate gene expression. Associates with chromatin at the NF-kappa-B promoter region via association with DDX1. Essential for cytokine gene expression in T-cells. The NF-kappa-B homodimeric RELA-RELA complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. Key transcription factor regulating the IFN response during SARS-CoV-2 infection. |
| Protein Name | Transcription Factor P65Nuclear Factor Nf-Kappa-B P65 SubunitNuclear Factor Of Kappa Light Polypeptide Gene Enhancer In B-Cells 3 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-1169091Reactome: R-HSA-1810476Reactome: R-HSA-193692Reactome: R-HSA-202424Reactome: R-HSA-209560Reactome: R-HSA-2559582Reactome: R-HSA-2871837Reactome: R-HSA-3134963Reactome: R-HSA-3214841Reactome: R-HSA-381340Reactome: R-HSA-445989Reactome: R-HSA-448706Reactome: R-HSA-4755510Reactome: R-HSA-5603029Reactome: R-HSA-5607761Reactome: R-HSA-5607764Reactome: R-HSA-5621575Reactome: R-HSA-5660668Reactome: R-HSA-844456Reactome: R-HSA-8853884Reactome: R-HSA-9020702Reactome: R-HSA-933542Reactome: R-HSA-9660826Reactome: R-HSA-9692916 |
| Cellular Localisation | NucleusCytoplasmNuclearBut Also Found In The Cytoplasm In An Inactive Form Complexed To An Inhibitor (I-Kappa-B)Colocalized With Ddx1 In The Nucleus Upon Tnf-Alpha InductionColocalizes With Gfi1 In The Nucleus After Lps StimulationTranslocation To The Nucleus Is Impaired In LMonocytogenes Infection |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Transcription Factor P65 antibodyAnti-Nuclear Factor Nf-Kappa-B P65 Subunit antibodyAnti-Nuclear Factor Of Kappa Light Polypeptide Gene Enhancer In B-Cells 3 antibodyAnti-RELA antibodyAnti-NFKB3 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance