| Host: |
Rabbit |
| Applications: |
WB/IF/ICC/ELISA |
| Reactivity: |
Human/Mouse/Rat |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Clonality: |
Polyclonal |
| Conjugation: |
Unconjugated |
| Isotype: |
IgG |
| Formulation: |
PBS with 0.02% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Purification: |
Affinity purification |
| Concentration: |
Lot specific |
| Dilution Range: |
WB:1:500-1:2000IF/ICC:1:100-1:200ELISA:Recommended starting concentration is 1 Mu g/mL. Please optimize the concentration based on your specific assay requirements. |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Gene Symbol: |
PDPK1 |
| Gene ID: |
5170 |
| Uniprot ID: |
PDPK1_HUMAN |
| Specificity: |
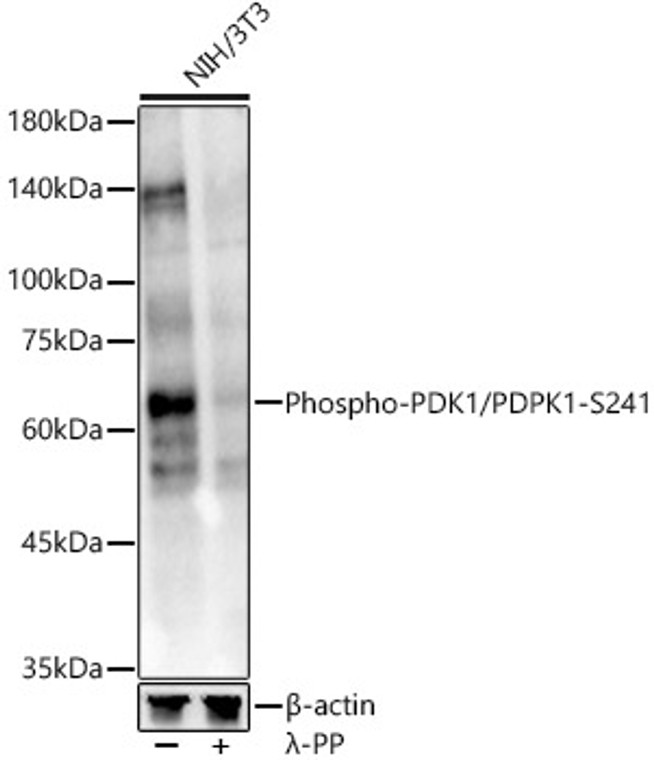
A phospho specific peptide corresponding to residues surrounding S241 of human PDK1/PDPK1 |
| Tissue Specificity | Appears to be expressed ubiquitously. The Tyr-9 phosphorylated form is markedly increased in diseased tissue compared with normal tissue from lung, liver, colon and breast. |
| Post Translational Modifications | Phosphorylation on Ser-241 in the activation loop is required for full activity. PDPK1 itself can autophosphorylate Ser-241, leading to its own activation. Autophosphorylation is inhibited by the apoptotic C-terminus cleavage product of PKN2. Tyr-9 phosphorylation is critical for stabilization of both PDPK1 and the PDPK1/SRC complex via HSP90-mediated protection of PDPK1 degradation. Angiotensin II stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of PDPK1 in vascular smooth muscle in a calcium- and SRC-dependent manner. Phosphorylated on Tyr-9, Tyr-373 and Tyr-376 by INSR in response to insulin. Palmitate negatively regulates autophosphorylation at Ser-241 and palmitate-induced phosphorylation at Ser-529 and Ser-501 by PKC/PRKCQ negatively regulates its ability to phosphorylate PKB/AKT1. Phosphorylation at Thr-354 by MELK partially inhibits kinase activity, the inhibition is cooperatively enhanced by phosphorylation at Ser-394 and Ser-398 by MAP3K5. Autophosphorylated.autophosphorylation is inhibited by the apoptotic C-terminus cleavage product of PKN2. Monoubiquitinated in the kinase domain, deubiquitinated by USP4. |
| Function | Serine/threonine kinase which acts as a master kinase, phosphorylating and activating a subgroup of the AGC family of protein kinases. Its targets include: protein kinase B (PKB/AKT1, PKB/AKT2, PKB/AKT3), p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RPS6KB1), p90 ribosomal protein S6 kinase (RPS6KA1, RPS6KA2 and RPS6KA3), cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PRKACA), protein kinase C (PRKCD and PRKCZ), serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK1, SGK2 and SGK3), p21-activated kinase-1 (PAK1), TSSK3, protein kinase PKN (PKN1 and PKN2). Plays a central role in the transduction of signals from insulin by providing the activating phosphorylation to PKB/AKT1, thus propagating the signal to downstream targets controlling cell proliferation and survival, as well as glucose and amino acid uptake and storage. Negatively regulates the TGF-beta-induced signaling by: modulating the association of SMAD3 and SMAD7 with TGF-beta receptor, phosphorylating SMAD2, SMAD3, SMAD4 and SMAD7, preventing the nuclear translocation of SMAD3 and SMAD4 and the translocation of SMAD7 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in response to TGF-beta. Activates PPARG transcriptional activity and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Activates the NF-kappa-B pathway via phosphorylation of IKKB. The tyrosine phosphorylated form is crucial for the regulation of focal adhesions by angiotensin II. Controls proliferation, survival, and growth of developing pancreatic cells. Participates in the regulation of Ca(2+) entry and Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels of mast cells. Essential for the motility of vascular endothelial cells (ECs) and is involved in the regulation of their chemotaxis. Plays a critical role in cardiac homeostasis by serving as a dual effector for cell survival and beta-adrenergic response. Plays an important role during thymocyte development by regulating the expression of key nutrient receptors on the surface of pre-T cells and mediating Notch-induced cell growth and proliferative responses. Provides negative feedback inhibition to toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappa-B activation in macrophages. Isoform 3: Catalytically inactive. |
| Protein Name | 3-Phosphoinositide-Dependent Protein Kinase 1Hpdk1 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-114604Reactome: R-HSA-1257604Reactome: R-HSA-165158Reactome: R-HSA-202424Reactome: R-HSA-2730905Reactome: R-HSA-2871837Reactome: R-HSA-354192Reactome: R-HSA-389357Reactome: R-HSA-392451Reactome: R-HSA-444257Reactome: R-HSA-5218920Reactome: R-HSA-5218921Reactome: R-HSA-5607764Reactome: R-HSA-5625740Reactome: R-HSA-5674400Reactome: R-HSA-6804757Reactome: R-HSA-9634635Reactome: R-HSA-9735871Reactome: R-HSA-9755779 |
| Cellular Localisation | CytoplasmNucleusCell MembranePeripheral Membrane ProteinCell JunctionFocal AdhesionTyrosine Phosphorylation Seems To Occur Only At The Cell MembraneTranslocates To The Cell Membrane Following Insulin Stimulation By A Mechanism That Involves Binding To Grb14 And InsrSrc And Hsp90 Promote Its Localization To The Cell MembraneIts Nuclear Localization Is Dependent On Its Association With Ptpn6 And Its Phosphorylation At Ser-396Restricted To The Nucleus In Neuronal Cells While In Non-Neuronal Cells It Is Found In The CytoplasmThe Ser-241 Phosphorylated Form Is Distributed Along The Perinuclear Region In Neuronal Cells While In Non-Neuronal Cells It Is Found In Both The Nucleus And The CytoplasmIgf1 Transiently Increases Phosphorylation At Ser-241 Of Neuronal Pdpk1Resulting In Its Translocation To Other Cellular CompartmentsThe Tyrosine-Phosphorylated Form Colocalizes With Ptk2b In Focal Adhesions After Angiotensin Ii Stimulation |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-3-Phosphoinositide-Dependent Protein Kinase 1 antibodyAnti-Hpdk1 antibodyAnti-PDPK1 antibodyAnti-PDK1 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance