| Host: |
Rabbit |
| Applications: |
WB/IHC |
| Reactivity: |
Human/Mouse/Rat |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
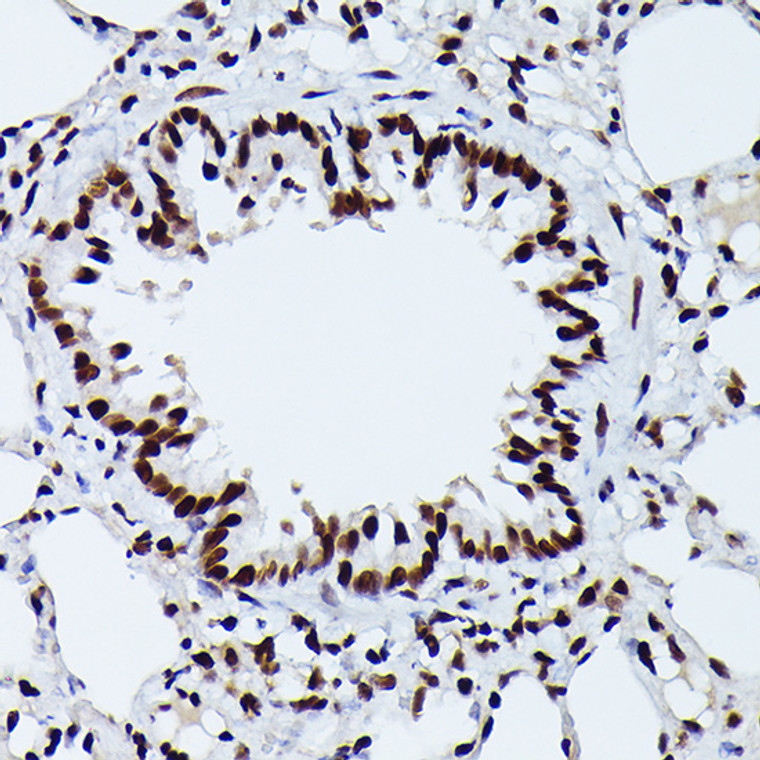
Rabbit monoclonal antibody anti-Phospho-NRF2-S40 is suitable for use in Western Blot and Immunohistochemistry research applications. |
| Clonality: |
Monoclonal |
| Clone ID: |
S0MR |
| Conjugation: |
Unconjugated |
| Isotype: |
IgG |
| Formulation: |
PBS with 0.02% Sodium Azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% Glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Purification: |
Affinity purification |
| Dilution Range: |
WB 1:500-1:2000IHC-P 1:50-1:200 |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Gene Symbol: |
NFE2L2 |
| Gene ID: |
4780 |
| Uniprot ID: |
NF2L2_HUMAN |
| Immunogen: |
A synthetic phosphorylated peptide around S40 of human NRF2 (Q16236). |
| Immunogen Sequence: |
DFSQR |
| Tissue Specificity | Widely expressed. Highest expression in adult muscle, kidney, lung, liver and in fetal muscle. |
| Post Translational Modifications | Ubiquitinated in the cytoplasm by the BCR(KEAP1) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex leading to its degradation. In response to oxidative stress, electrophile metabolites, such as sulforaphane, modify KEAP1, leading to inhibit activity of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, promoting NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and activity. In response to autophagy, the BCR(KEAP1) complex is inactivated. Phosphorylation of Ser-40 by PKC in response to oxidative stress dissociates NFE2L2 from its cytoplasmic inhibitor KEAP1, promoting its translocation into the nucleus. Acetylation at Lys-596 and Lys-599 increases nuclear localization whereas deacetylation by SIRT1 enhances cytoplasmic presence. Glycation impairs transcription factor activity by preventing heterodimerization with small Maf proteins. Deglycation by FN3K restores activity. |
| Function | Transcription factor that plays a key role in the response to oxidative stress: binds to antioxidant response (ARE) elements present in the promoter region of many cytoprotective genes, such as phase 2 detoxifying enzymes, and promotes their expression, thereby neutralizing reactive electrophiles. In normal conditions, ubiquitinated and degraded in the cytoplasm by the BCR(KEAP1) complex. In response to oxidative stress, electrophile metabolites inhibit activity of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, promoting nuclear accumulation of NFE2L2/NRF2, heterodimerization with one of the small Maf proteins and binding to ARE elements of cytoprotective target genes. The NFE2L2/NRF2 pathway is also activated in response to selective autophagy: autophagy promotes interaction between KEAP1 and SQSTM1/p62 and subsequent inactivation of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, leading to NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and expression of cytoprotective genes. May also be involved in the transcriptional activation of genes of the beta-globin cluster by mediating enhancer activity of hypersensitive site 2 of the beta-globin locus control region. Also plays an important role in the regulation of the innate immune response and antiviral cytosolic DNA sensing. It is a critical regulator of the innate immune response and survival during sepsis by maintaining redox homeostasis and restraint of the dysregulation of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways like MyD88-dependent and -independent and TNF-alpha signaling. Suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking pro-inflammatory cytokine transcription and the induction of IL6. Binds to the proximity of pro-inflammatory genes in macrophages and inhibits RNA Pol II recruitment. The inhibition is independent of the NRF2-binding motif and reactive oxygen species level. Represses antiviral cytosolic DNA sensing by suppressing the expression of the adapter protein STING1 and decreasing responsiveness to STING1 agonists while increasing susceptibility to infection with DNA viruses. Once activated, limits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infection and to virus-derived ligands through a mechanism that involves inhibition of IRF3 dimerization. Also inhibits both SARS-CoV-2 replication, as well as the replication of several other pathogenic viruses including Herpes Simplex Virus-1 and-2, Vaccinia virus, and Zika virus through a type I interferon (IFN)-independent mechanism. |
| Protein Name | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2Nf-E2-Related Factor 2Nfe2-Related Factor 2Nrf-2Hebp1Nuclear Factor - Erythroid Derived 2 - Like 2 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-8951664Reactome: R-HSA-9679191Reactome: R-HSA-9707587Reactome: R-HSA-9707616Reactome: R-HSA-9755511Reactome: R-HSA-9759194Reactome: R-HSA-9762114Reactome: R-HSA-9818025Reactome: R-HSA-9818027Reactome: R-HSA-9818028Reactome: R-HSA-9818749 |
| Cellular Localisation | CytoplasmCytosolNucleusCytosolic Under Unstressed Conditions: Ubiquitinated And Degraded By The Bcr(Keap1) E3 Ubiquitin Ligase ComplexTranslocates Into The Nucleus Upon Induction By Electrophilic Agents That Inactivate The Bcr(Keap1) E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Complex |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 antibodyAnti-Nf-E2-Related Factor 2 antibodyAnti-Nfe2-Related Factor 2 antibodyAnti-Nrf-2 antibodyAnti-Hebp1 antibodyAnti-Nuclear Factor - Erythroid Derived 2 - Like 2 antibodyAnti-NFE2L2 antibodyAnti-NRF2 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance