| Host: |
Rabbit |
| Applications: |
WB |
| Reactivity: |
Human |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
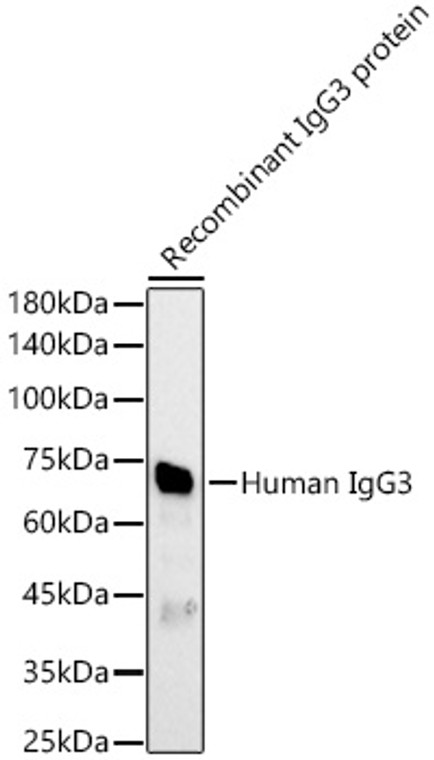
Rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-Immunoglobulin Heavy Constant Gamma 3 is suitable for use in Western Blot research applications. |
| Clonality: |
Polyclonal |
| Conjugation: |
Unconjugated |
| Isotype: |
IgG |
| Formulation: |
PBS with 0.02% Sodium Azide, 0.05% BSA, 50% Glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Purification: |
Affinity purification |
| Dilution Range: |
WB 1:100-1:500 |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Gene Symbol: |
IGHG3Uniprot ID=IGHG3_HUMAN" |
| Immunogen: |
Recombinant protein of human IgG3. |
| Immunogen Sequence: |
VHTFPAVLQSSGLYSLSSVV TVPSSSLGTQTYTCNVNHKP SNTKVDKRVELKTPLGDTTH TCPRCPEPKSCDTPPPCPRC PEPKSCDTPPPCPRCPEPKS C |
| Post Translational Modifications | N-linked glycans at Asn-322 are noncore fucosylated and the vast majority are diantennary species with a bisecting GlcNAc. Among them the most dominant glycans are HexNAc5Hex4, HexNAc5Hex5, and HexNAc5Hex5Sia1. N-linked glycans at Asn-227 are diantennary core fucosylated structures without bisecting GlcNAc (HexNAc4Hex4Fuc1, HexNAc4Hex5Fuc1, and HexNAc4Hex5Fuc1Sia1). Glycosylation on Asn-227 is required for interaction with Fc receptors and ability to activate the complement pathway. (Microbial infection) Deglycosylation on Asn-227 by S.pyogenes EndoS or Endos2 endoglucosidases prevents interaction between immunoglobulin-gamma (IgG) and Fc receptors, impairing ability to activate the complement pathway. O-linked glycans are non-, mono- and disialylated core 1-type O-glycans. |
| Function | Constant region of immunoglobulin heavy chains. Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are membrane-bound or secreted glycoproteins produced by B lymphocytes. In the recognition phase of humoral immunity, the membrane-bound immunoglobulins serve as receptors which, upon binding of a specific antigen, trigger the clonal expansion and differentiation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulins-secreting plasma cells. Secreted immunoglobulins mediate the effector phase of humoral immunity, which results in the elimination of bound antigens. The antigen binding site is formed by the variable domain of one heavy chain, together with that of its associated light chain. Thus, each immunoglobulin has two antigen binding sites with remarkable affinity for a particular antigen. The variable domains are assembled by a process called V-(D)-J rearrangement and can then be subjected to somatic hypermutations which, after exposure to antigen and selection, allow affinity maturation for a particular antigen. |
| Protein Name | Immunoglobulin Heavy Constant Gamma 3HdcHeavy Chain Disease ProteinIg Gamma-3 Chain C Region |
| Cellular Localisation | Isoform 1: SecretedIsoform 2: Cell MembraneSingle-Pass Membrane Protein |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Immunoglobulin Heavy Constant Gamma 3 antibodyAnti-Hdc antibodyAnti-Heavy Chain Disease Protein antibodyAnti-Ig Gamma-3 Chain C Region antibodyAnti-IGHG3 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance