| Host: |
Rabbit |
| Applications: |
WB/IF/IP |
| Reactivity: |
Human/Mouse/Rat |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
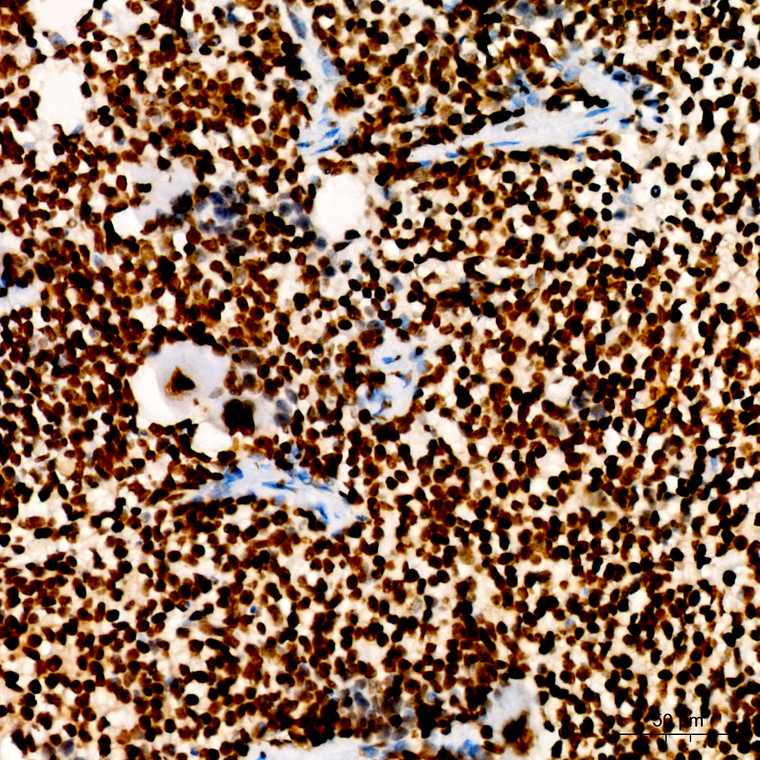
Rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-Di-Methyl-Histone H3-K27 (16-37) is suitable for use in Western Blot, Immunofluorescence and Immunoprecipitation research applications. |
| Clonality: |
Polyclonal |
| Conjugation: |
Unconjugated |
| Isotype: |
IgG |
| Formulation: |
PBS with 0.02% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Purification: |
Affinity purification |
| Dilution Range: |
WB 1:500-1:1000IF/ICC 1:50-1:200IP 1:50-1:200ChIP 1:20-1:100ChIP-seq 1:20-1:100 |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Immunogen Region: |
16-37 |
| Immunogen: |
A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence within amino acids 16-37 of human histone H3 (NP_003520.1). |
| Immunogen Sequence: |
APRKQLATKAARKSAPATGG VK |
| Background | Enables damaged DNA binding activity and single-stranded DNA binding activity. Involved in DNA repair and DNA replication. Part of DNA replication factor A complex. |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance