| Host: |
Mouse |
| Applications: |
WB/IF/FC/ELISA |
| Reactivity: |
Human |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
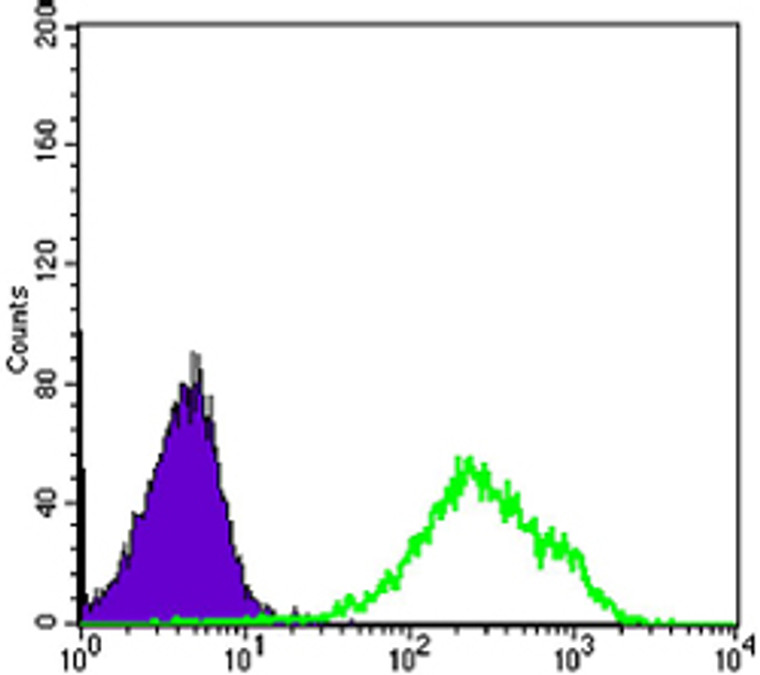
Mouse monoclonal antibody anti-Death domain-associated protein 6 is suitable for use in Western Blot, Immunofluorescence, Flow Cytometry and ELISA research applications. |
| Clonality: |
Monoclonal |
| Clone ID: |
7A11 |
| Conjugation: |
Unconjugated |
| Isotype: |
IgG1 |
| Formulation: |
Liquid in PBS containing 50% Glycerol and 0.03% Sodium Azide. |
| Purification: |
Antibody are purified by protein G affinity chromatography. |
| Concentration: |
1 mg/mL |
| Dilution Range: |
WB 1:500-1:2000IF 1:200-1:1000FC 1:200-1:400ELISA 1:10000 |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Gene Symbol: |
DAXX |
| Gene ID: |
1616 |
| Uniprot ID: |
DAXX_HUMAN |
| Specificity: |
Daxx Monoclonal Antibody detects endogenous levels of Daxx protein. |
| Immunogen: |
Purified recombinant fragment of human Daxx expressed in E. Coli. |
| Post Translational Modifications | Sumoylated with SUMO1 on multiple lysine residues. Phosphorylated by HIPK1 upon glucose deprivation. Polyubiquitinated.which is promoted by CUL3 and SPOP and results in proteasomal degradation. Ubiquitinated by MDM2.inducing its degradation. Deubiquitinated by USP7.leading to stabilize it. |
| Function | Transcription corepressor known to repress transcriptional potential of several sumoylated transcription factors. Down-regulates basal and activated transcription. Its transcription repressor activity is modulated by recruiting it to subnuclear compartments like the nucleolus or PML/POD/ND10 nuclear bodies through interactions with MCSR1 and PML, respectively. Seems to regulate transcription in PML/POD/ND10 nuclear bodies together with PML and may influence TNFRSF6-dependent apoptosis thereby. Inhibits transcriptional activation of PAX3 and ETS1 through direct protein-protein interactions. Modulates PAX5 activity.the function seems to involve CREBBP. Acts as an adapter protein in a MDM2-DAXX-USP7 complex by regulating the RING-finger E3 ligase MDM2 ubiquitination activity. Under non-stress condition, in association with the deubiquitinating USP7, prevents MDM2 self-ubiquitination and enhances the intrinsic E3 ligase activity of MDM2 towards TP53, thereby promoting TP53 ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Upon DNA damage, its association with MDM2 and USP7 is disrupted, resulting in increased MDM2 autoubiquitination and consequently, MDM2 degradation, which leads to TP53 stabilization. Acts as histone chaperone that facilitates deposition of histone H3.3. Acts as targeting component of the chromatin remodeling complex ATRX:DAXX which has ATP-dependent DNA translocase activity and catalyzes the replication-independent deposition of histone H3.3 in pericentric DNA repeats outside S-phase and telomeres, and the in vitro remodeling of H3.3-containing nucleosomes. Does not affect the ATPase activity of ATRX but alleviates its transcription repression activity. Upon neuronal activation associates with regulatory elements of selected immediate early genes where it promotes deposition of histone H3.3 which may be linked to transcriptional induction of these genes. Required for the recruitment of histone H3.3:H4 dimers to PML-nuclear bodies (PML-NBs).the process is independent of ATRX and facilitated by ASF1A.PML-NBs are suggested to function as regulatory sites for the incorporation of newly synthesized histone H3.3 into chromatin. In case of overexpression of centromeric histone variant CENPA (as found in various tumors) is involved in its mislocalization to chromosomes.the ectopic localization involves a heterotypic tetramer containing CENPA, and histones H3.3 and H4 and decreases binding of CTCF to chromatin. Proposed to mediate activation of the JNK pathway and apoptosis via MAP3K5 in response to signaling from TNFRSF6 and TGFBR2. Interaction with HSPB1/HSP27 may prevent interaction with TNFRSF6 and MAP3K5 and block DAXX-mediated apoptosis. In contrast, in lymphoid cells JNC activation and TNFRSF6-mediated apoptosis may not involve DAXX. Shows restriction activity towards human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). Plays a role as a positive regulator of the heat shock transcription factor HSF1 activity during the stress protein response. |
| Protein Name | Death Domain-Associated Protein 6DaxxHdaxxEts1-Associated Protein 1Eap1Fas Death Domain-Associated Protein |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-3899300Reactome: R-HSA-6804757Reactome: R-HSA-9609690Reactome: R-HSA-9670095Reactome: R-HSA-9670613Reactome: R-HSA-9670615 |
| Cellular Localisation | CytoplasmNucleusNucleoplasmPml BodyNucleolusChromosomeCentromereDispersed Throughout The NucleoplasmIn Pml/Pod/Nd10 Nuclear BodiesAnd In Nucleoli (Probable)Colocalizes With Histone H33AtrxHira And Asf1a At Pml-Nuclear BodiesColocalizes With A Subset Of Interphase CentromeresBut Is Absent From Mitotic CentromeresDetected In Cytoplasmic Punctate StructuresTranslocates From The Nucleus To The Cytoplasm Upon Glucose Deprivation Or Oxidative StressColocalizes With Rassf1 In The NucleusColocalizes With Usp7 In Nucleoplasma With Accumulation In Speckled StructuresIsoform Beta: NucleusDiffuse Nuclear Distribution Pattern And No Comparable Dot-Like Accumulation Of Isoform 1Isoform Gamma: Nucleus |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Death Domain-Associated Protein 6 antibodyAnti-Daxx antibodyAnti-Hdaxx antibodyAnti-Ets1-Associated Protein 1 antibodyAnti-Eap1 antibodyAnti-Fas Death Domain-Associated Protein antibodyAnti-DAXX antibodyAnti-BING2 antibodyAnti-DAP6 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance
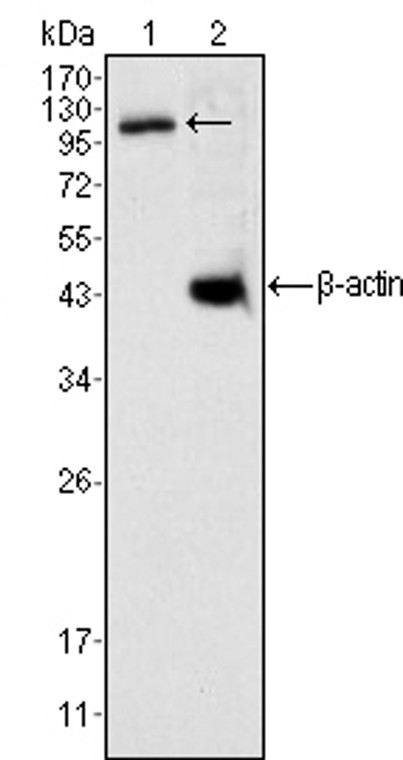







![Anti-Daxx antibody [DAXX-01] (STJ16100577) Anti-Daxx antibody [DAXX-01] (STJ16100577)](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-zso2xnchw9/images/stencil/300x300/products/149294/346834/STJ16100577_1__07484.1681998957.jpg?c=1)
