| Host: |
Rabbit |
| Applications: |
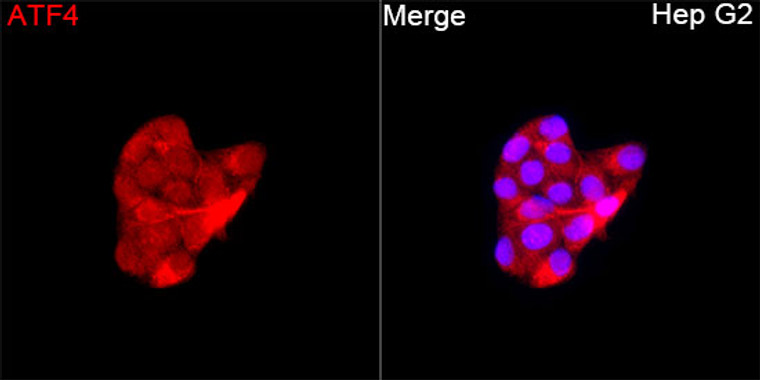
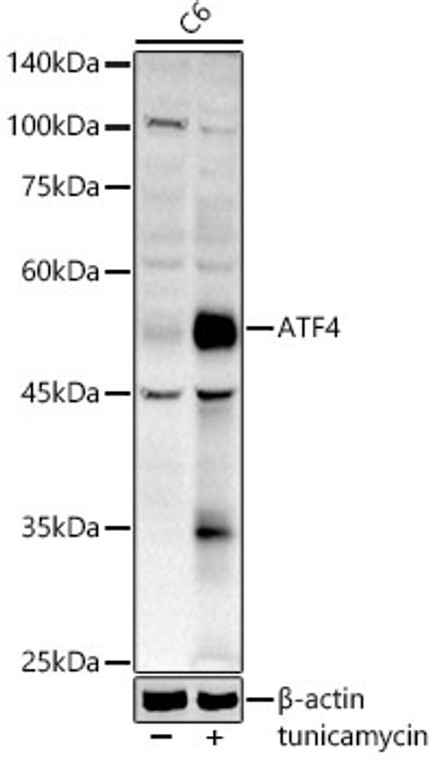
WB/IF |
| Reactivity: |
Human/Mouse/Rat |
| Note: |
STRICTLY FOR FURTHER SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH USE ONLY (RUO). MUST NOT TO BE USED IN DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC APPLICATIONS. |
| Short Description: |
Rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-Cyclic Amp-Dependent Transcription Factor Atf-4 (260-351) is suitable for use in Western Blot and Immunofluorescence research applications. |
| Clonality: |
Polyclonal |
| Conjugation: |
Unconjugated |
| Isotype: |
IgG |
| Formulation: |
PBS with 0.05% Proclin300, 50% Glycerol, pH7.3. |
| Purification: |
Affinity purification |
| Dilution Range: |
WB 1:100-1:500IF/ICC 1:50-1:200 |
| Storage Instruction: |
Store at-20°C for up to 1 year from the date of receipt, and avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Gene Symbol: |
ATF4 |
| Gene ID: |
468 |
| Uniprot ID: |
ATF4_HUMAN |
| Immunogen Region: |
260-351 |
| Immunogen: |
Recombinant fusion protein containing a sequence corresponding to amino acids 260-351 of human ATF4 (NP_877962.1). |
| Immunogen Sequence: |
PYDPPGEKMVAAKVKGEKLD KKLKKMEQNKTAATRYRQKK RAEQEALTGECKELEKKNEA LKERADSLAKEIQYLKDLIE EVRKARGKKRVP |
| Post Translational Modifications | Ubiquitinated by SCF(BTRC) in response to mTORC1 signal, followed by proteasomal degradation and leading to down-regulate expression of SIRT4. Interaction with EP300/p300 inhibits ubiquitination by SCF(BTRC). Phosphorylation at Ser-245 by RPS6KA3/RSK2 in osteoblasts enhances transactivation activity and promotes osteoblast differentiation. Phosphorylated on the betaTrCP degron motif at Ser-219, followed by phosphorylation at Thr-213, Ser-224, Ser-231, Ser-235 and Ser-248, promoting interaction with BTRC and ubiquitination. Phosphorylation is promoted by mTORC1. Phosphorylation at Ser-215 by CK2 decreases its stability. Phosphorylated by NEK6. Hydroxylated by PHD3, leading to decreased protein stability. |
| Function | Transcription factor that binds the cAMP response element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGTACAG-3') and displays two biological functions, as regulator of metabolic and redox processes under normal cellular conditions, and as master transcription factor during integrated stress response (ISR). Binds to asymmetric CRE's as a heterodimer and to palindromic CRE's as a homodimer. Core effector of the ISR, which is required for adaptation to various stress such as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, amino acid starvation, mitochondrial stress or oxidative stress. During ISR, ATF4 translation is induced via an alternative ribosome translation re-initiation mechanism in response to EIF2S1/eIF-2-alpha phosphorylation, and stress-induced ATF4 acts as a master transcription factor of stress-responsive genes in order to promote cell recovery. Promotes the transcription of genes linked to amino acid sufficiency and resistance to oxidative stress to protect cells against metabolic consequences of ER oxidation. Activates the transcription of NLRP1, possibly in concert with other factors in response to ER stress. Activates the transcription of asparagine synthetase (ASNS) in response to amino acid deprivation or ER stress. However, when associated with DDIT3/CHOP, the transcriptional activation of the ASNS gene is inhibited in response to amino acid deprivation. Together with DDIT3/CHOP, mediates programmed cell death by promoting the expression of genes involved in cellular amino acid metabolic processes, mRNA translation and the terminal unfolded protein response (terminal UPR), a cellular response that elicits programmed cell death when ER stress is prolonged and unresolved. Together with DDIT3/CHOP, activates the transcription of the IRS-regulator TRIB3 and promotes ER stress-induced neuronal cell death by regulating the expression of BBC3/PUMA in response to ER stress. May cooperate with the UPR transcriptional regulator QRICH1 to regulate ER protein homeostasis which is critical for cell viability in response to ER stress. In the absence of stress, ATF4 translation is at low levels and it is required for normal metabolic processes such as embryonic lens formation, fetal liver hematopoiesis, bone development and synaptic plasticity. Acts as a regulator of osteoblast differentiation in response to phosphorylation by RPS6KA3/RSK2: phosphorylation in osteoblasts enhances transactivation activity and promotes expression of osteoblast-specific genes and post-transcriptionally regulates the synthesis of Type I collagen, the main constituent of the bone matrix. Cooperates with FOXO1 in osteoblasts to regulate glucose homeostasis through suppression of beta-cell production and decrease in insulin production. Activates transcription of SIRT4. Regulates the circadian expression of the core clock component PER2 and the serotonin transporter SLC6A4. Binds in a circadian time-dependent manner to the cAMP response elements (CRE) in the SLC6A4 and PER2 promoters and periodically activates the transcription of these genes. Mainly acts as a transcriptional activator in cellular stress adaptation, but it can also act as a transcriptional repressor: acts as a regulator of synaptic plasticity by repressing transcription, thereby inhibiting induction and maintenance of long-term memory. Regulates synaptic functions via interaction with DISC1 in neurons, which inhibits ATF4 transcription factor activity by disrupting ATF4 dimerization and DNA-binding. (Microbial infection) Binds to a Tax-responsive enhancer element in the long terminal repeat of HTLV-I. |
| Protein Name | Cyclic Amp-Dependent Transcription Factor Atf-4Camp-Dependent Transcription Factor Atf-4Activating Transcription Factor 4Cyclic Amp-Responsive Element-Binding Protein 2Creb-2Camp-Responsive Element-Binding Protein 2Tax-Responsive Enhancer Element-Binding Protein 67Taxreb67 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-380994Reactome: R-HSA-381042Reactome: R-HSA-381183Reactome: R-HSA-9633012Reactome: R-HSA-9648895Reactome: R-HSA-9818027 |
| Cellular Localisation | NucleusNucleus SpeckleCytoplasmCell MembraneCytoskeletonMicrotubule Organizing CenterCentrosomeColocalizes With Gabbr1 In Hippocampal Neuron Dendritic MembranesColocalizes With Nek6 At The CentrosomeRecruited To Nuclear Speckles Following Interaction With Ep300/P300 |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Cyclic Amp-Dependent Transcription Factor Atf-4 antibodyAnti-Camp-Dependent Transcription Factor Atf-4 antibodyAnti-Activating Transcription Factor 4 antibodyAnti-Cyclic Amp-Responsive Element-Binding Protein 2 antibodyAnti-Creb-2 antibodyAnti-Camp-Responsive Element-Binding Protein 2 antibodyAnti-Tax-Responsive Enhancer Element-Binding Protein 67 antibodyAnti-Taxreb67 antibodyAnti-ATF4 antibodyAnti-CREB2 antibodyAnti-TXREB antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org
12 months for antibodies. 6 months for ELISA Kits. Please see website T&Cs for further guidance