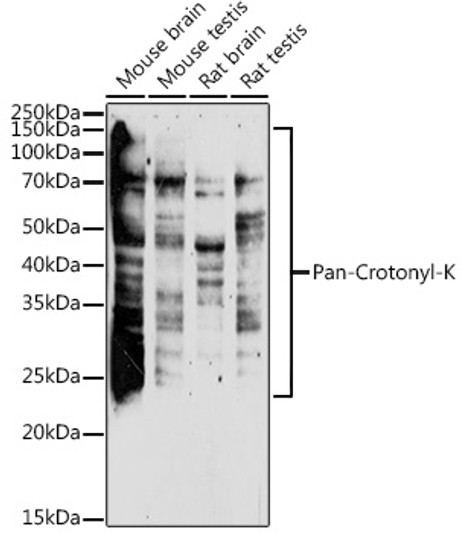
| Background | Lysine crotonylation (Kcr) was first discovered about 10 years ago, as a PTM of histone. It was revealed that Kcr is an evolutionarily conserved and common PTM that occurs in both core histone and some non-histone proteins in a variety of organisms. Similar to other types of PTM, Kcr is a reversible modification. The classic histone acetyltransferases (HATs) , p300/CBP, PCAF, and MOF, are responsible for most crotonylation events, while the histone deacetylases (HDACs) HDAC1/2/3 and SIRT1/2/3 reverse these reactions. The chromodomain protein CDYL acts as a crotonyl-CoA hydratase to negatively regulate histone Kcr by reducing substrate supply. CDYL-regulated Kcr of RPA1 plays an important role in homologous recombination (HR)-mediated DNA repair (23) , while HDAC-regulated histone crotonylation is reduced after DNA damage. |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org