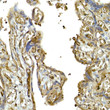
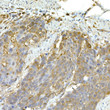
| Tissue Specificity | Widely expressed, at a low level. Expression is detected at slightly highest levels in placenta, pancreas and spleen and at barely levels in detectable brain, testis and lung. |
| Post Translational Modifications | Sumoylated. Sumoylation positively regulates its role in type I interferon induction and is enhanced by PIAS2-beta. Ubiquitinated by RNF125, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. USP17/UPS17L2-dependent deubiquitination positively regulates the receptor. Ubiquitinated by TRIM25 via 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination, promoting activation of IFIH1/MDA5. Ubiquitinated by TRIM40 via 'Lys-48'-linked ubiquitination.leading to proteasomal degradation. Ubiquitinated by TRIM65 via 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination, promoting activation of IFIH1/MDA5. ISGylated by ISG15. ISGylation increases upon infection with dengue (DENV) or Zika (ZIKV) viruses. ISGylation at Lys-23 and Lys-43 is dependent of dephosphorylation at Ser-88, regulates mitochondrial translocation and oligomerization. Essential for IFIH1/MDA5-mediated cytokine responses and restriction of virus replication. Phosphorylated at Ser-88. Dephosphorylated by phosphatases PPP11CA/PPP11CC.dephosphorylation precedes and is required for ISGylation. During apoptosis, processed into 3 cleavage products. The helicase-containing fragment, once liberated from the CARD domains, translocate from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. The processed protein significantly sensitizes cells to DNA degradation. (Microbial infection) Cleaved and inactivated by the protease 2A of coxsackievirus B3, poliovirus and enterovirus 71 allowing the virus to disrupt the host type I interferon production. |
| Function | Innate immune receptor which acts as a cytoplasmic sensor of viral nucleic acids and plays a major role in sensing viral infection and in the activation of a cascade of antiviral responses including the induction of type I interferons and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Its ligands include mRNA lacking 2'-O-methylation at their 5' cap and long-dsRNA (>1 kb in length). Upon ligand binding it associates with mitochondria antiviral signaling protein (MAVS/IPS1) which activates the IKK-related kinases: TBK1 and IKBKE which phosphorylate interferon regulatory factors: IRF3 and IRF7 which in turn activate transcription of antiviral immunological genes, including interferons (IFNs).IFN-alpha and IFN-beta. Responsible for detecting the Picornaviridae family members such as encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV), mengo encephalomyocarditis virus (ENMG), and rhinovirus. Detects coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Can also detect other viruses such as dengue virus (DENV), west Nile virus (WNV), and reovirus. Also involved in antiviral signaling in response to viruses containing a dsDNA genome, such as vaccinia virus. Plays an important role in amplifying innate immune signaling through recognition of RNA metabolites that are produced during virus infection by ribonuclease L (RNase L). May play an important role in enhancing natural killer cell function and may be involved in growth inhibition and apoptosis in several tumor cell lines. |
| Protein Name | Interferon-Induced Helicase C Domain-Containing Protein 1Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis Autoantigen 140 KdaCadm-140 AutoantigenHelicase With 2 Card DomainsHelicardInterferon-Induced With Helicase C Domain Protein 1Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Protein 5Mda-5Murabutide Down-Regulated ProteinRig-I-Like Receptor 2Rlr-2Rna Helicase-Dead Box Protein 116 |
| Database Links | Reactome: R-HSA-168928Reactome: R-HSA-5689880Reactome: R-HSA-5689896Reactome: R-HSA-918233Reactome: R-HSA-933541Reactome: R-HSA-933542Reactome: R-HSA-933543Reactome: R-HSA-936440Reactome: R-HSA-9692916Reactome: R-HSA-9705671Reactome: R-HSA-9833109Reactome: R-HSA-9909505 |
| Cellular Localisation | CytoplasmNucleusMitochondrionUpon Viral Rna Stimulation And IsgylationTranslocates From Cytosol To MitochondrionMay Be Found In The NucleusDuring Apoptosis |
| Alternative Antibody Names | Anti-Interferon-Induced Helicase C Domain-Containing Protein 1 antibodyAnti-Clinically Amyopathic Dermatomyositis Autoantigen 140 Kda antibodyAnti-Cadm-140 Autoantigen antibodyAnti-Helicase With 2 Card Domains antibodyAnti-Helicard antibodyAnti-Interferon-Induced With Helicase C Domain Protein 1 antibodyAnti-Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Protein 5 antibodyAnti-Mda-5 antibodyAnti-Murabutide Down-Regulated Protein antibodyAnti-Rig-I-Like Receptor 2 antibodyAnti-Rlr-2 antibodyAnti-Rna Helicase-Dead Box Protein 116 antibodyAnti-IFIH1 antibodyAnti-MDA5 antibodyAnti-RH116 antibody |
Information sourced from Uniprot.org