Related articles
Secondary antibodies resources
Alexa Fluor secondary antibodies
Biotinylated secondary antibodies
Enhancing Detection of Low-Abundance Proteins
9 tips for detecting phosphorylation events using a Western Blot
Western Blotting with Tissue Lysates
Immunohistochemistry introduction
Immunohistochemistry and Immunocytochemistry
Immunohistochemistry troubleshooter
Chromogenic and Fluorescent detection
Preparing paraffin-embedded and frozen samples for Immunohistochemistry
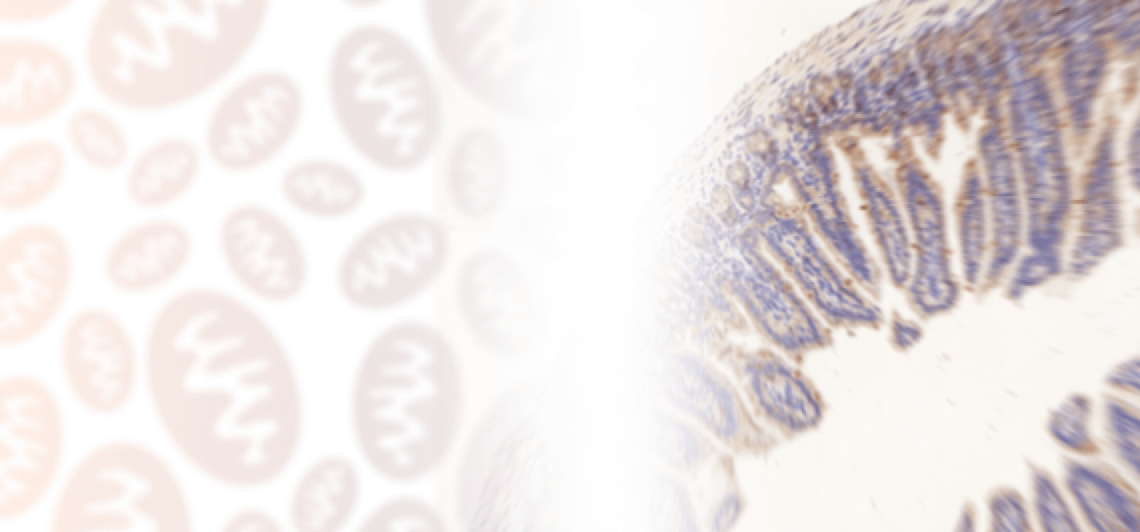
Immunohistochemistry protocol
Immunohistochemistry is a way of detecting antigens in tissue cells using the specific antigen-antibody binding. This type of binding can be observed by using different enzymes like HRP or AP, that effectively catalyse the reaction, which results in colour changes.
Sample preparation for tissue sample
Sharp knife and scissors to be used in order to avoid damage
Calcifications and fat tissues should be removed
Samples from live specimens should be fixated immediately after washing
Normal tissue can be used as a control, necrotic regions are not preferred.
Paraffin-embedding and freezing have to be preformed shortly after sectioning. If this is not possible, the tissues have to be stored at -70C.
Fixation
Immersion method:
This type of fixation immerses the tissue in a fixing solution for a set period of time, that corresponds to the type of solution and the stability of the antigen. Immersion is usually used for non-irrigation tissues like biopsies and surgical specimens.
Irrigation method:
The advantage of this technique is that it allows for quick and full fixation. Also, the irrigation method is quite suitable for animal experiments, because it efficiently lowers the interference of endogenous peroxidase.
Tips for fixations:
Avoid over-fixing the tissues and ensure that they are fresh following this procedure.
Using enough fixing solution and carefully washing all of it after fixation is advised.
Pre-treating the slide
This procedure prevents any peeling to the slide caused by radiation, pressure and temperature abnormalities.
For microscopic slide:
To remove the oil from the slide, place it in cleaning solution overnight or up to 24 hours. Wash in distilled water 5 times, dip in 95% isopropyl alcohol and dry.
For coverslip:
The procedure is the same as for the microscopic slide, with the only difference being the timing. Because the coverslip is significantly thinner, the cleaning should be performed in less than 2 hours.
Processing
Cells on coverslip:
Place the settled coverslip in a perforated plate or culture bottle.
When the cell growth reaches 60%, the coverslip can be removed.
Following the removal, fix the coverslip with cold acetone or paraformaldehyde 4% for up to 30 min.
Cell smear:
Retrieve non-adherent cells and wash 2x with cold PBS buffer.
Resuspend cells in PBS buffer, add 50nL to slide and smear evenly.
Air dry the slide and cover it paraformaldehyde 4% for 4 hours.
Blocking and Inactivation
Endogenous HRP inactivation:
Incubate the paraffin embedded section in 3% H2O2 for 10 minutes.
Incubate the frozen or cell section in 3% H2O2 and methanol solution for 30minutes.
Endogenous AP inactivation:
Sample has to be incubated in 0.1 mM Levamisole.
